Common Layer Properties
Table of Contents
All layers in Ventuz feature certain properties to control how layers are sized, composited, used masks, applied effects and so on, regardless if they are 2D, 3D or other types of layers. You can find an in-depth description of all these options on this page, for references about the different types of layers in Ventuz and their specific properties, check 2D Layers, 3D Layers and Other layers.
Blending
Blending operations, including modes, opacity and masking, can be switched ON or OFF for each individual layer by left-clicking close to the Blending caption. If the check mark appears, the blending operation, including opacity, mode and mask, is calculated for the current layer. If the check mark does not appear in front of the Blending options, the blending operations are not calculated.
As with all Layer Properties, in order to expand the Blending Options, click on the little arrow. A dropdown list of the supported blending modes will appear:
With the Blending Modes you control how the pixel values of the current layer are combined with those of the layers rendered before, i.e. the layers which are above the current layer. The bottom one is always in front of the rest.
Mode
Normal: The default Blending mode. When selected, only Layer Opacity settings are taken into account to composite the layer.
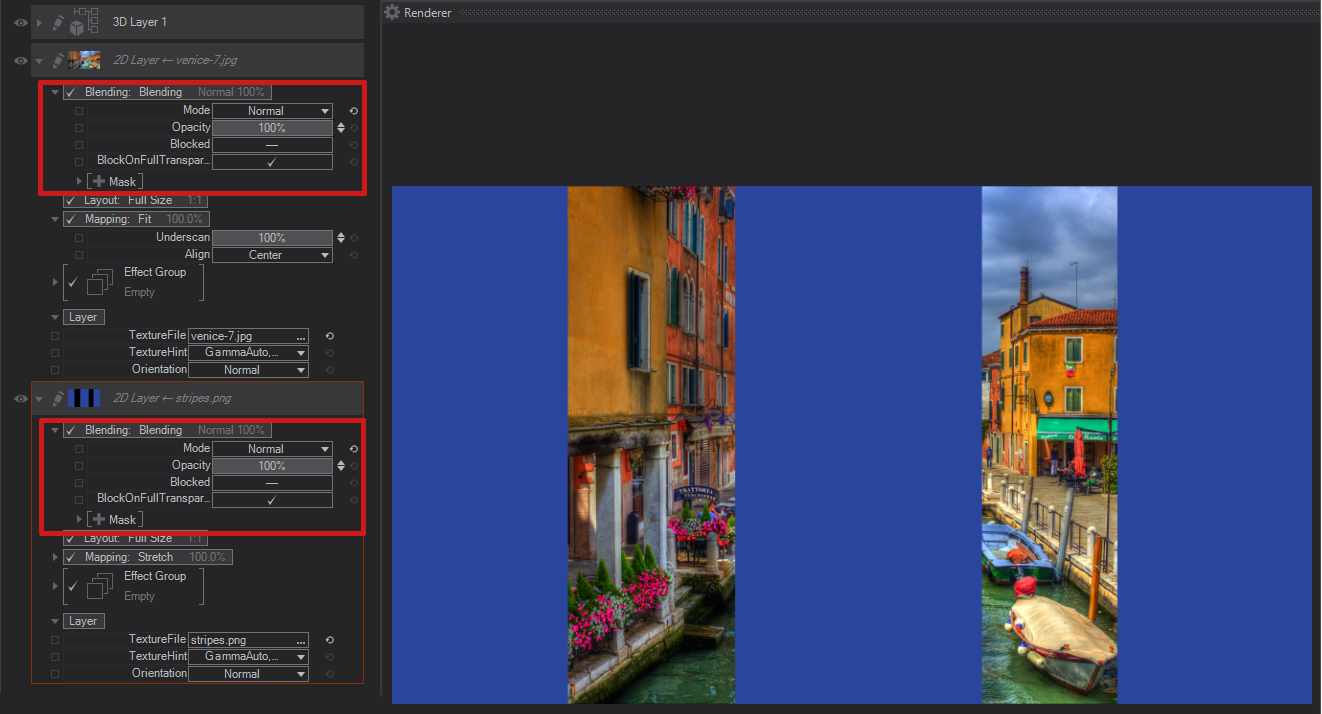
Darken: Compares the color information in both the current and the layer below and selects the darker pixels. Pixels lighter than the blend color are replaced, and pixels darker than the blend color do not change.
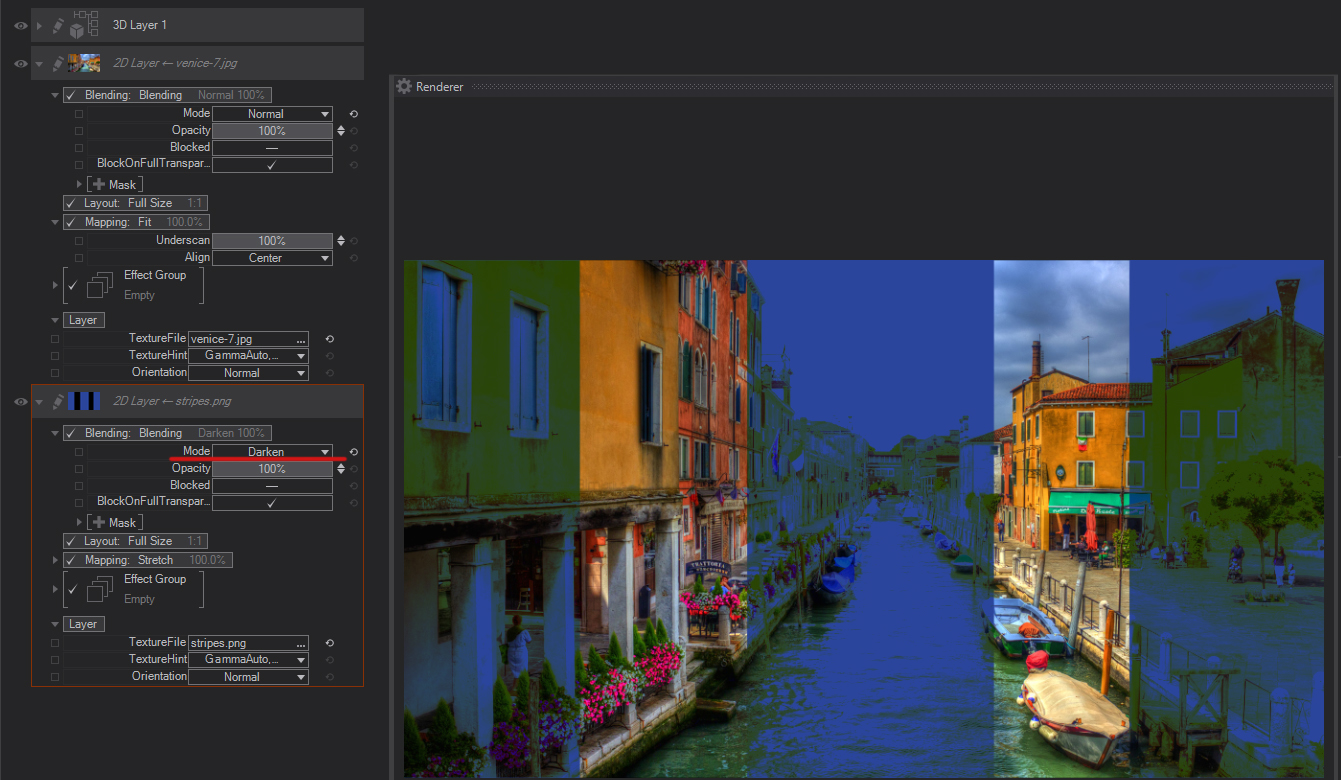
Multiply: Checks the color information and multiplies its values in both the upper foreground and the background layer. The resulting color is always a darker color. Multiplying any color with black produces black. Multiplying any color with white leaves the color unchanged. When you’re blending with a color other than black or white, successive blends produce progressively darker colors. The effect is similar to drawing on the image with multiple marking pens.
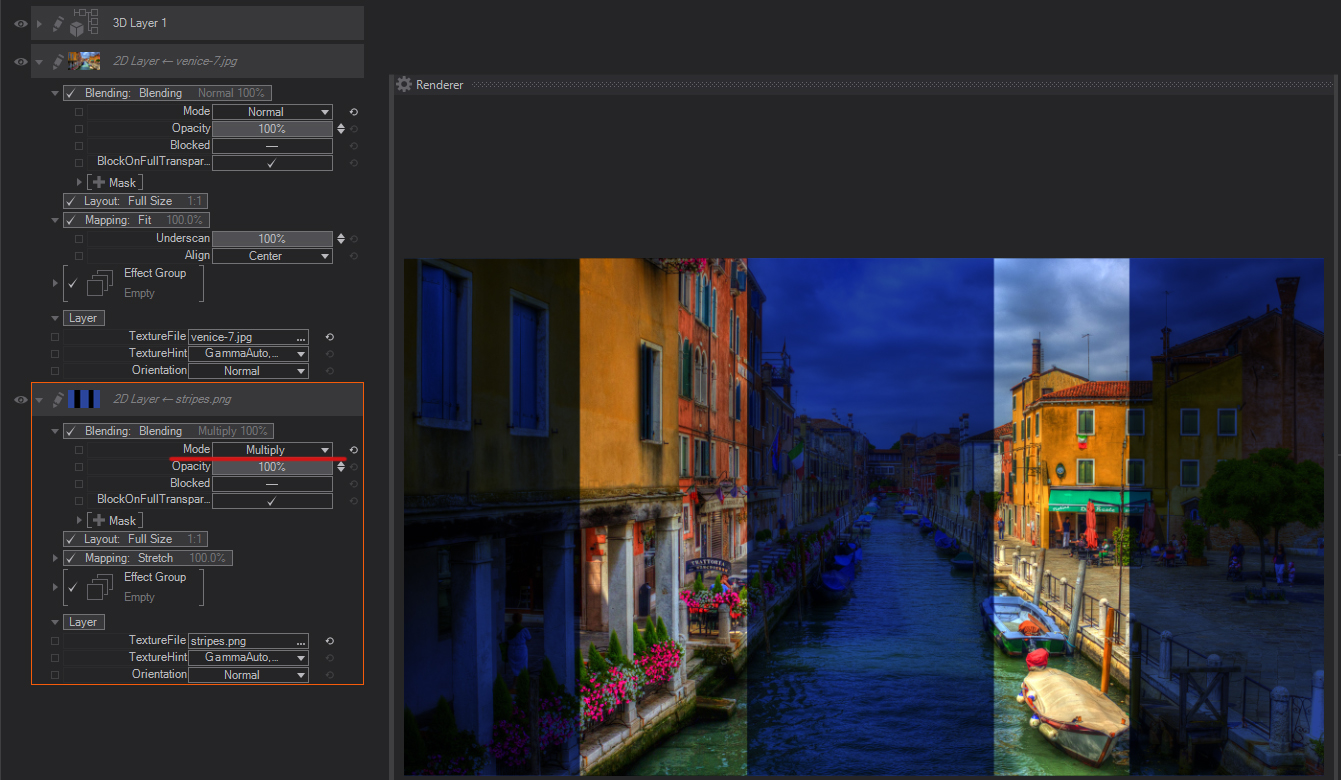
Color Burn: Looks at the color information in each channel and darkens the base color to reflect the blend color by increasing the contrast between the two. Blending with white produces no change.
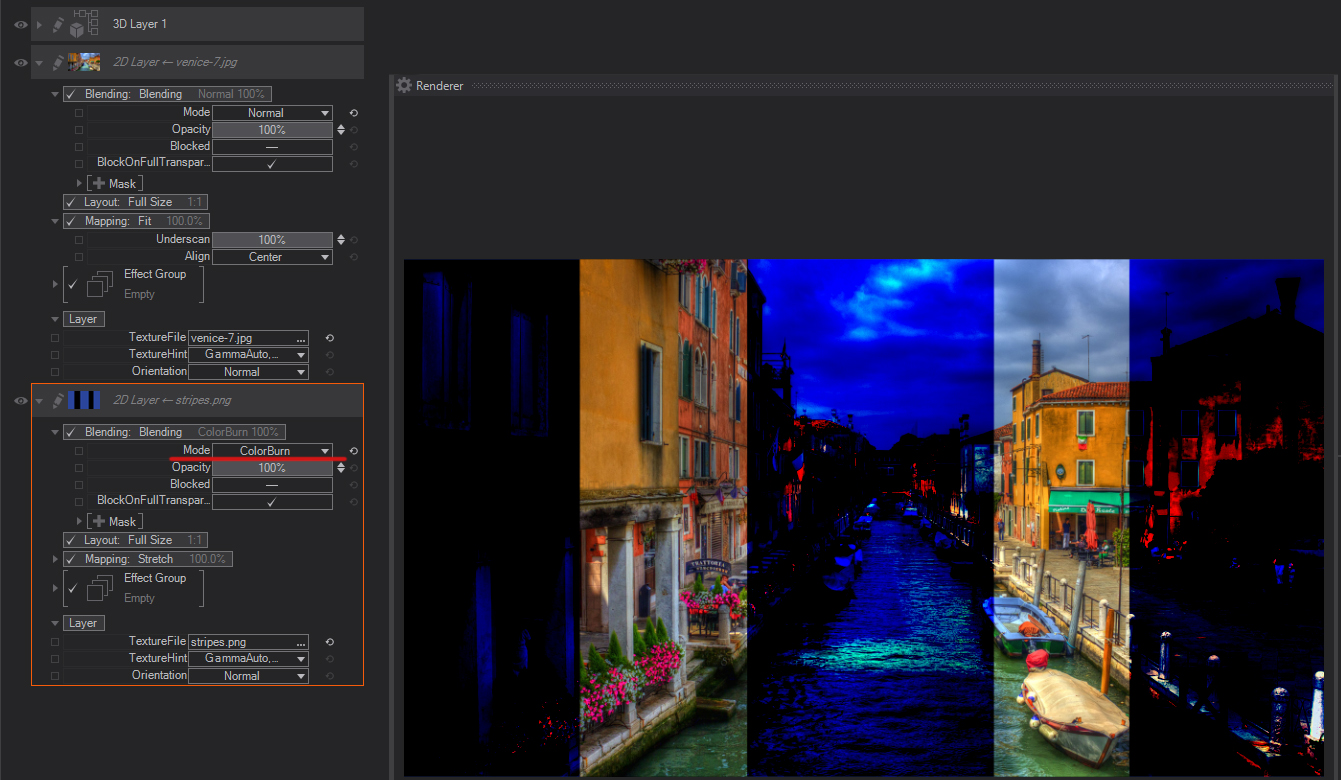
Linear Burn: Looks at the color information in each channel and darkens the base color to reflect the blend color by decreasing the brightness. Blending with white produces no change.
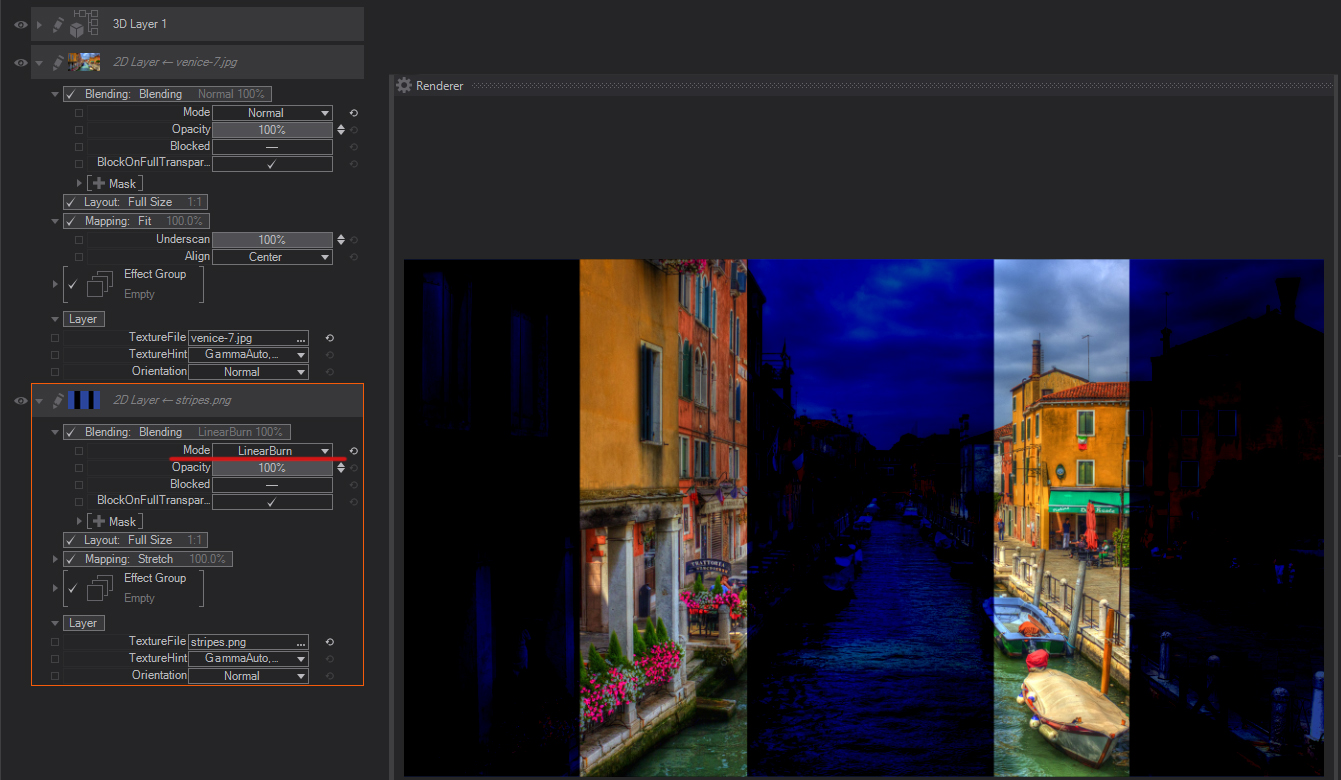
Darker Color: Compares the total of all channel values for the blend and base color and displays the lower value color. Darker Color does not produce a third color, which can result from the Darken blend because it chooses the lowest channel values from both the base and the blend color to create the resulting color.
Lighten: Looks at the color information in each channel and selects the base or blend color —whichever is lighter— as the resulting color. Pixels darker than the blend color are replaced, and pixels lighter than the blend color do not change.
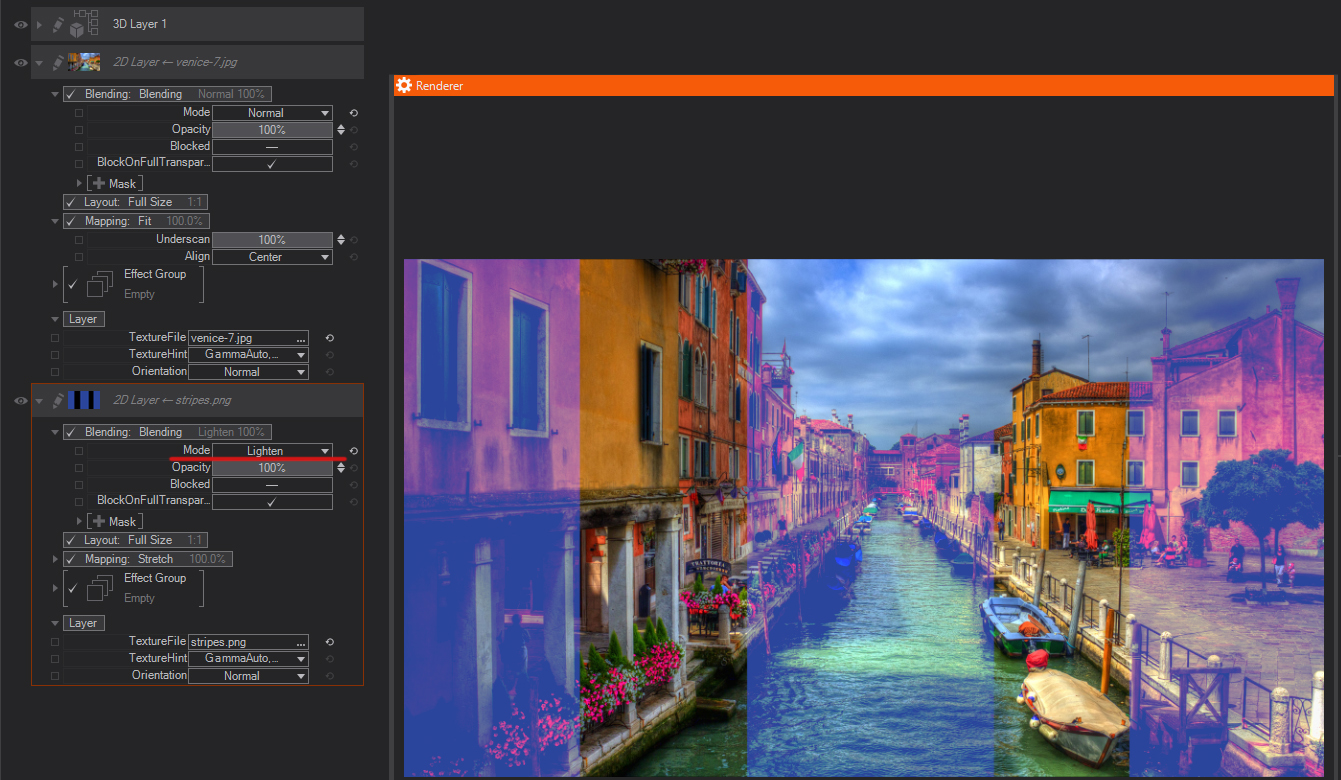
Screen: Looks at each channel’s color information and multiplies the inverse of the blend and base colors. The resulting color is always a lighter color. Screening with black leaves the color unchanged. Screening with white produces white. The effect is similar to projecting multiple photographic slides on top of each other.
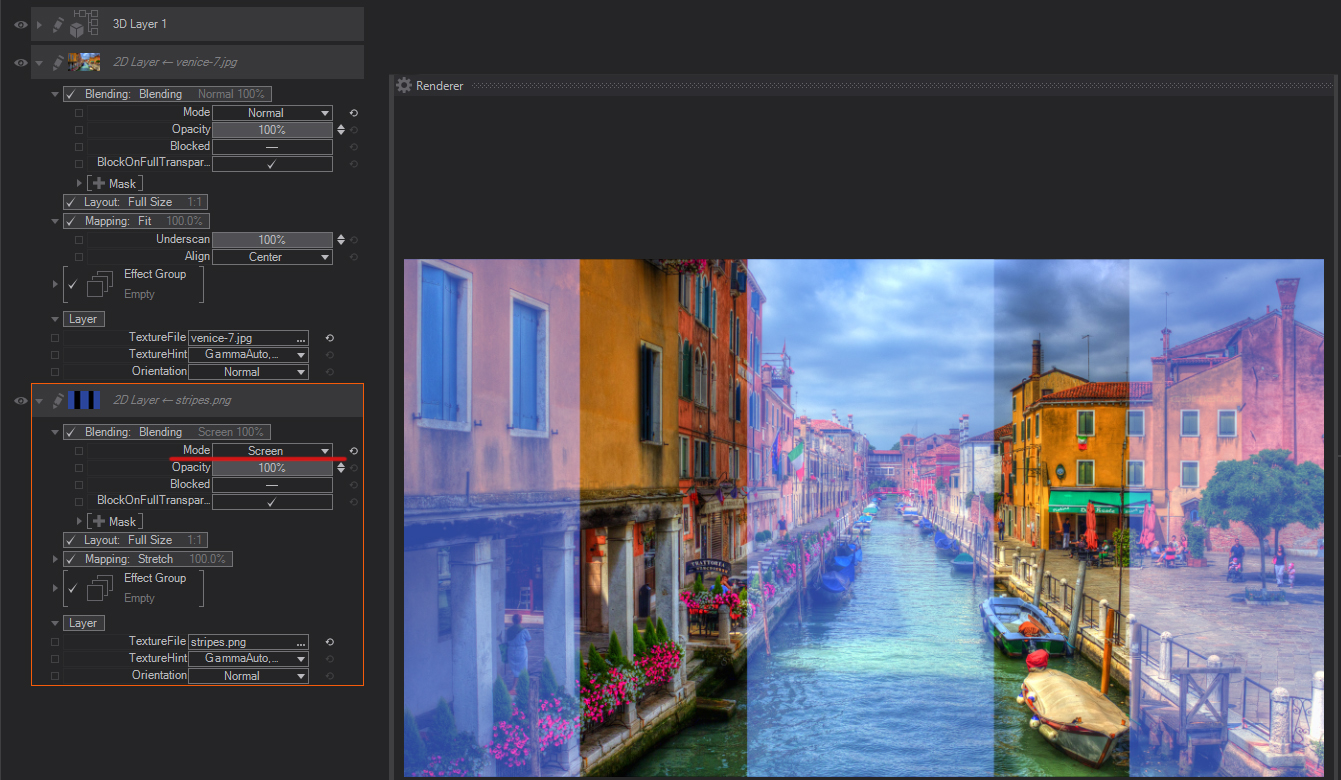
Color Dodge: Looks at the color information in each channel and brightens the base color to reflect the blend color by decreasing contrast between the two. Blending with black produces no change.
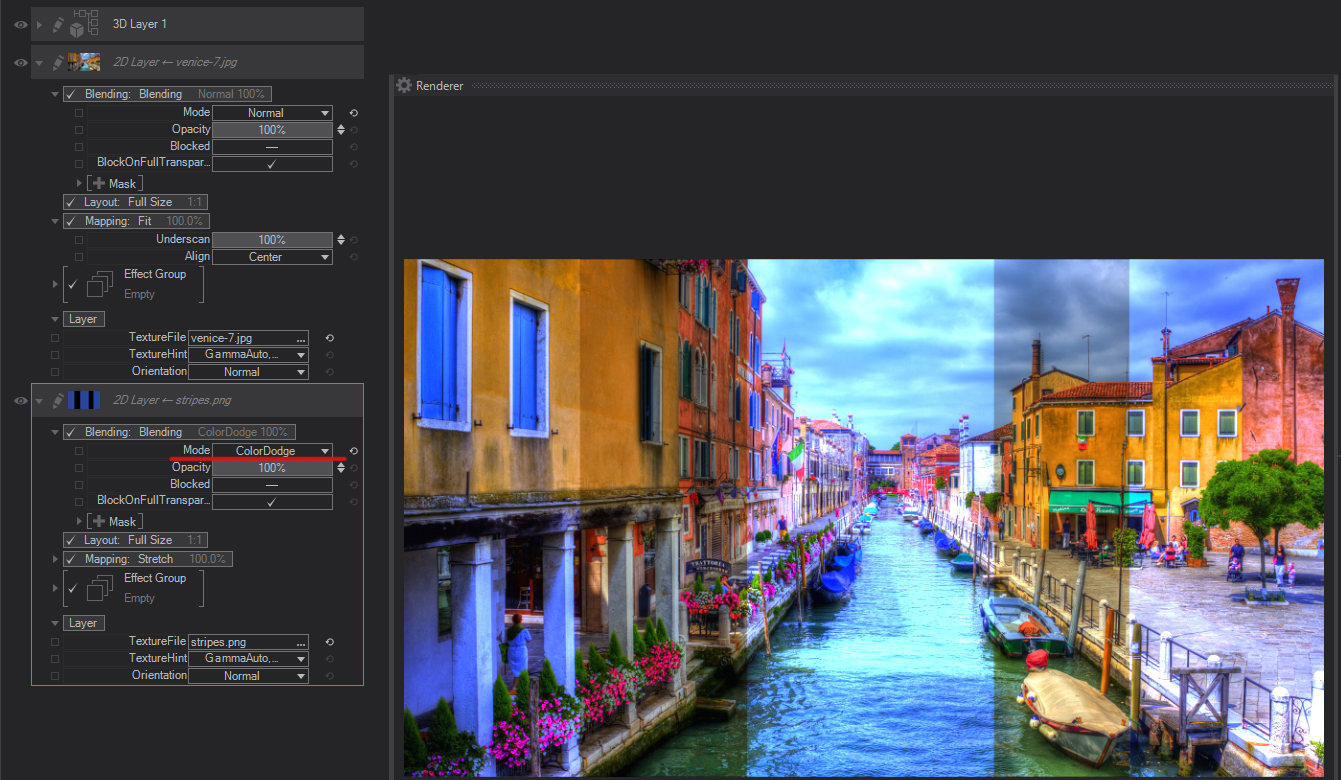
Linear Dodge (Add): Looks at the color information in each channel and brightens the base color to reflect the blend color by decreasing contrast between the two. Blending with black produces no change.
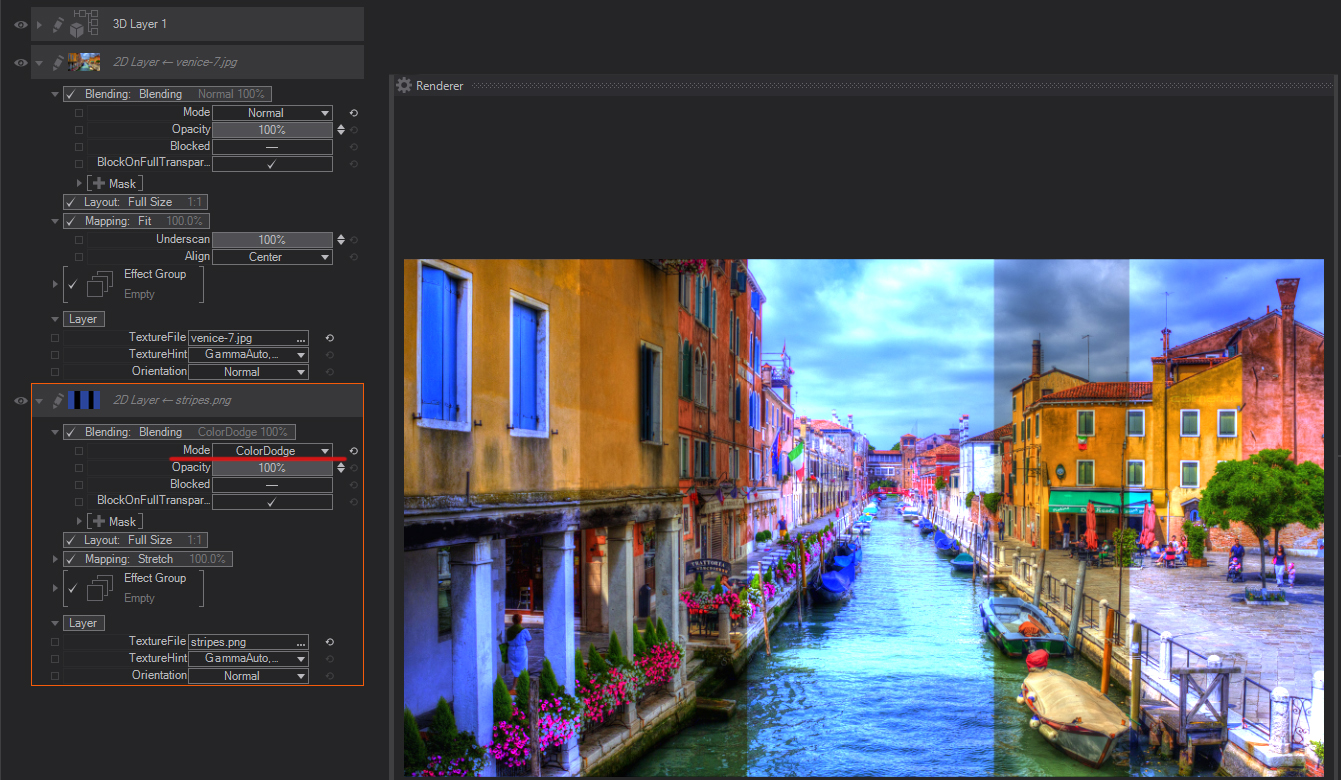
Lighter Color: Compares the total of all channel values for the blend and base color and displays the higher value color. Lighter Color does not produce a third color, which can result from the Lighten blend because it chooses the highest channel values from both the base and blend color to create the resulting color.
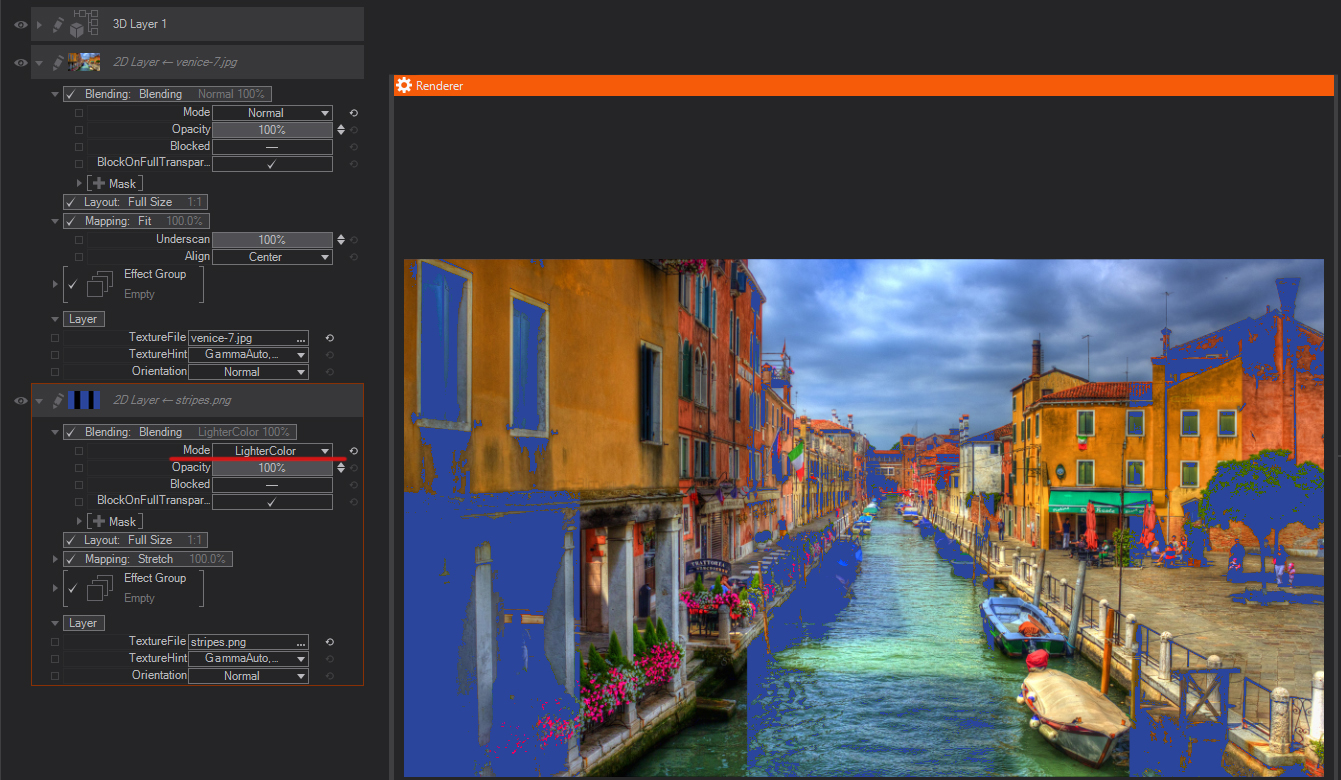
Overlay: Multiplies or screens the colors, depending on the base color. Patterns or color overlays the existing pixels while preserving the highlights and shadows of the base color. The base color is not replaced but mixed with the blending color to reflect the lightness or darkness of the original color.
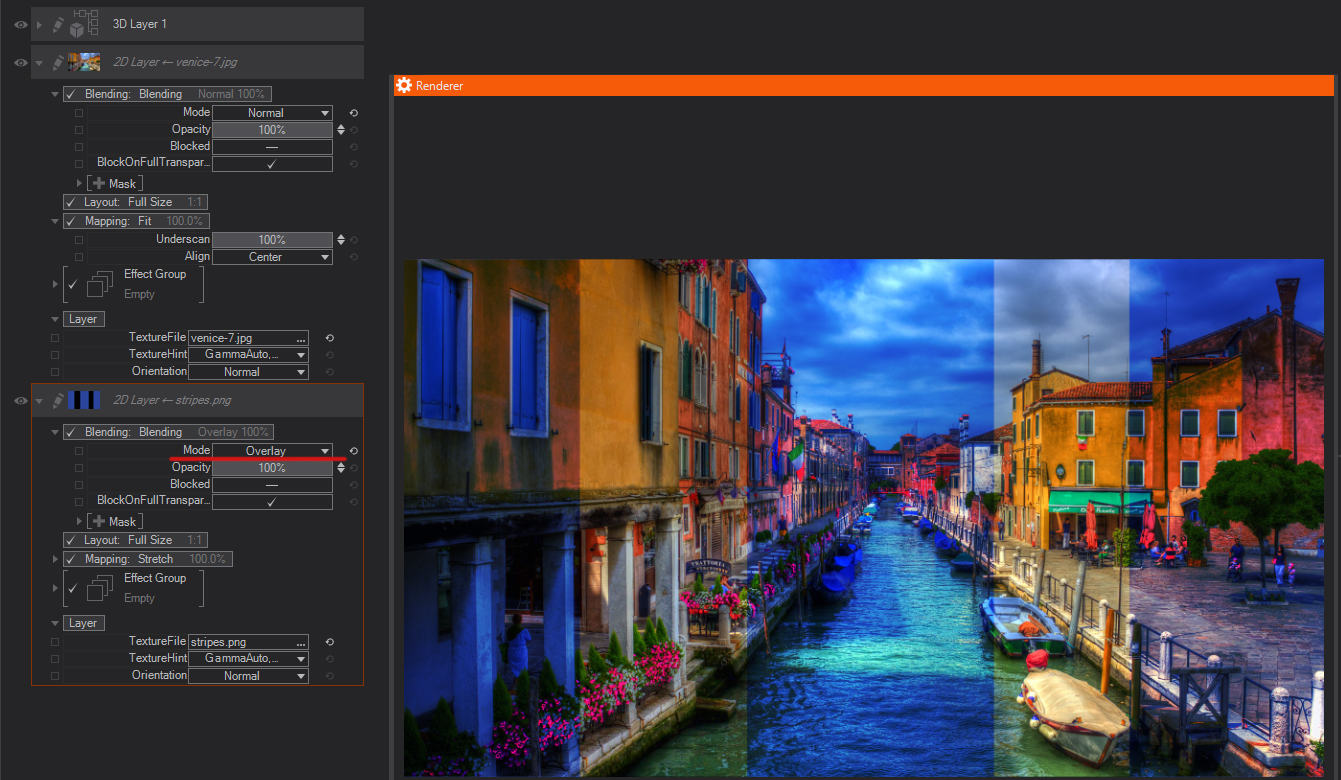
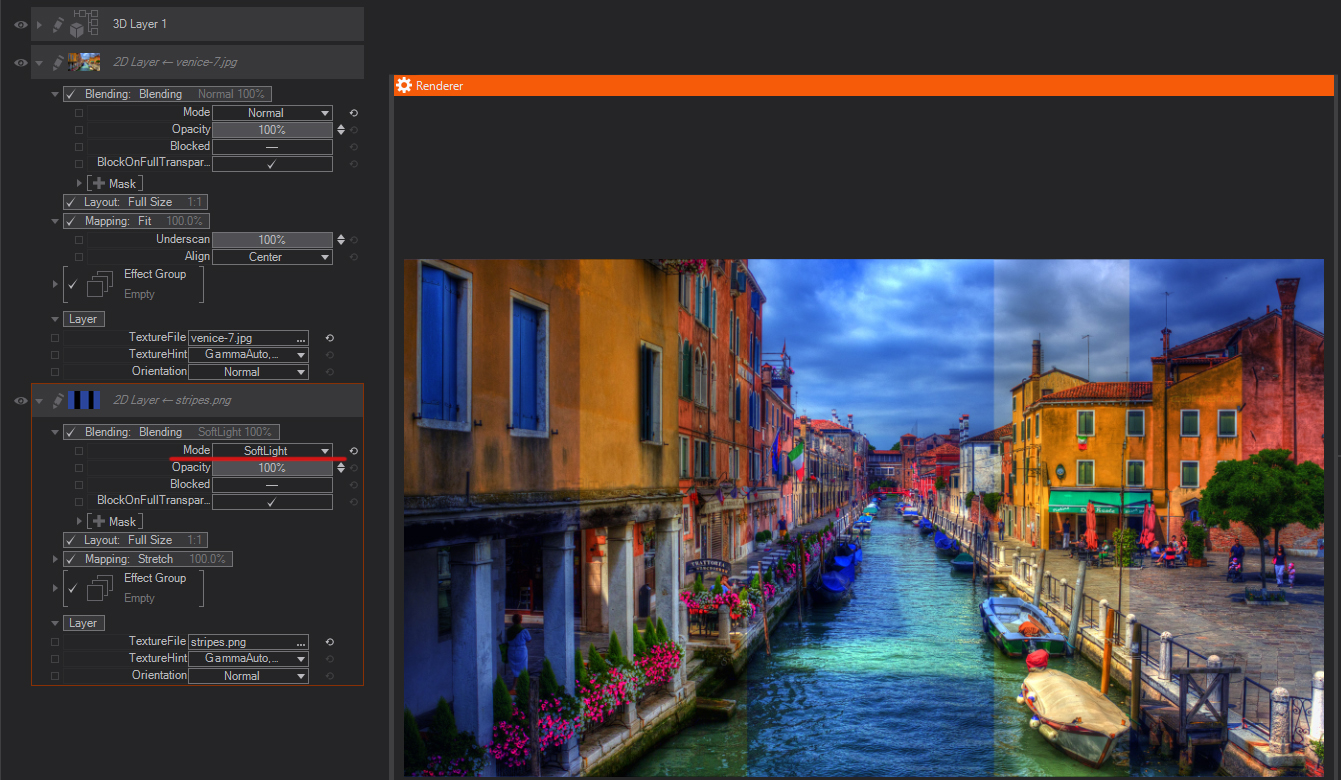
Soft Light: Darkens or lightens the colors, depending on the blending color. The effect is similar to shining a diffused spotlight on the image. If the blend color (light source) is lighter than 50% gray, the image is lightened as if it were dodged. If the blend color is darker than 50% gray, the image is darkened as if it were burned in. Blending with pure black or white produces a distinctly darker or lighter area, but does not result in pure black or white.
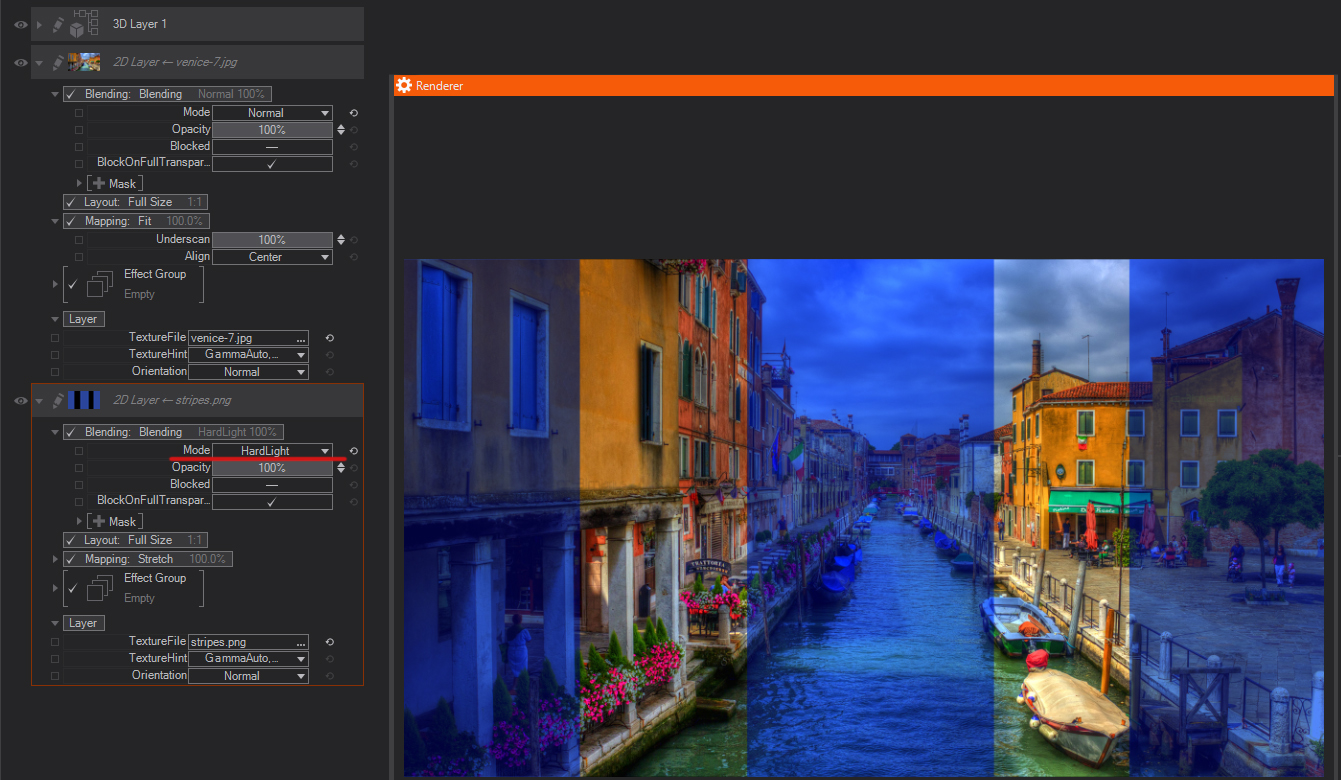
Hard Light: Multiplies or screens the colors, depending on the blending color. The effect is similar to shining a harsh spotlight on the image. If the blend color (light source) is lighter than 50% gray, the image is lightened, as if it were screened. This is useful for adding highlights to an image. If the blend color is darker than 50% gray, the image is darkened, as if it were multiplied. This is useful for adding shadows to an image. Blending with pure black or white results in pure black or white.
Vivid Light: Burns or dodges the colors by increasing or decreasing the contrast, depending on the blend color. If the blend color (light source) is lighter than 50% gray, the image is lightened by decreasing the contrast. If the blend color is darker than 50% gray, the image is darkened by increasing the contrast.
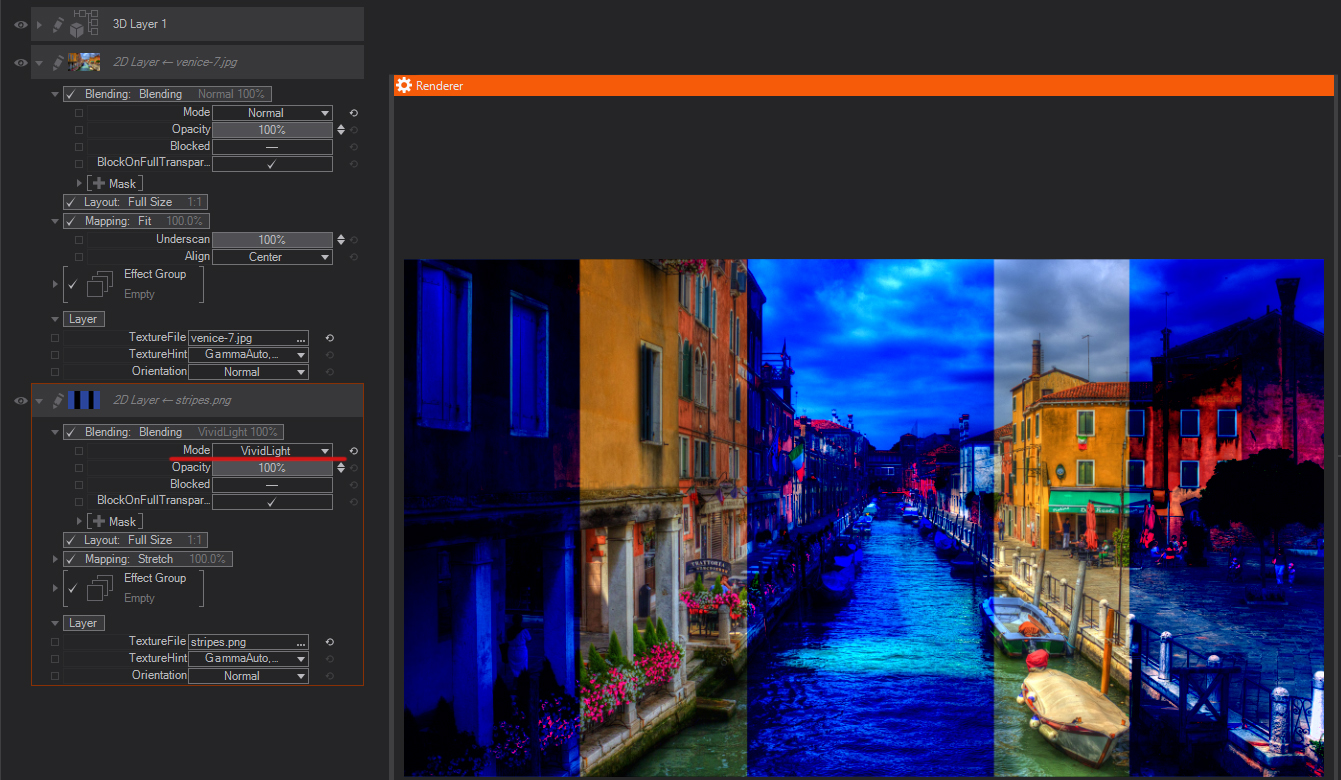
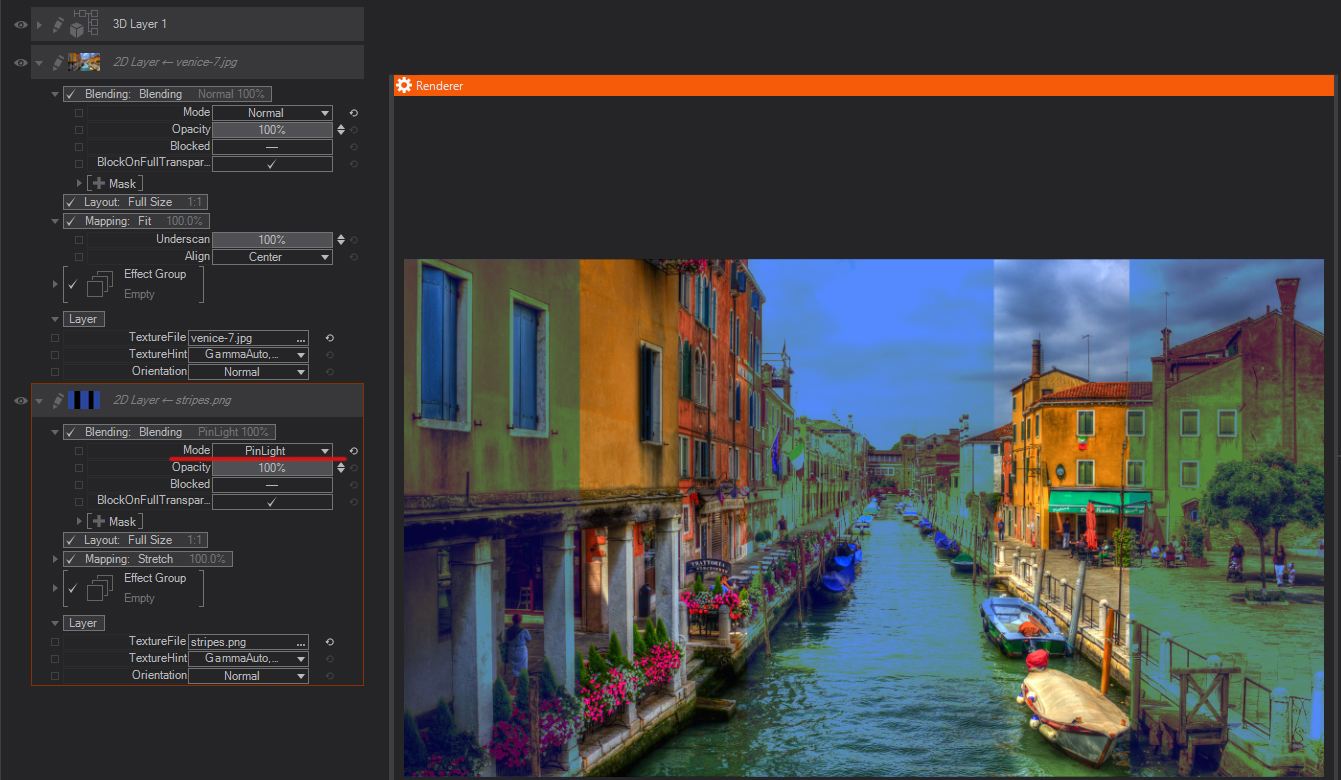
Pin Light: Replaces the colors, depending on the blend color. If the blend color (light source) is lighter than 50% gray, pixels darker than the blend color are replaced, and pixels lighter than the blend color do not change. If the blend color is darker than 50% gray, pixels lighter than the blend color are replaced, and pixels darker than the blend color do not change. This is useful for adding special effects to an image.
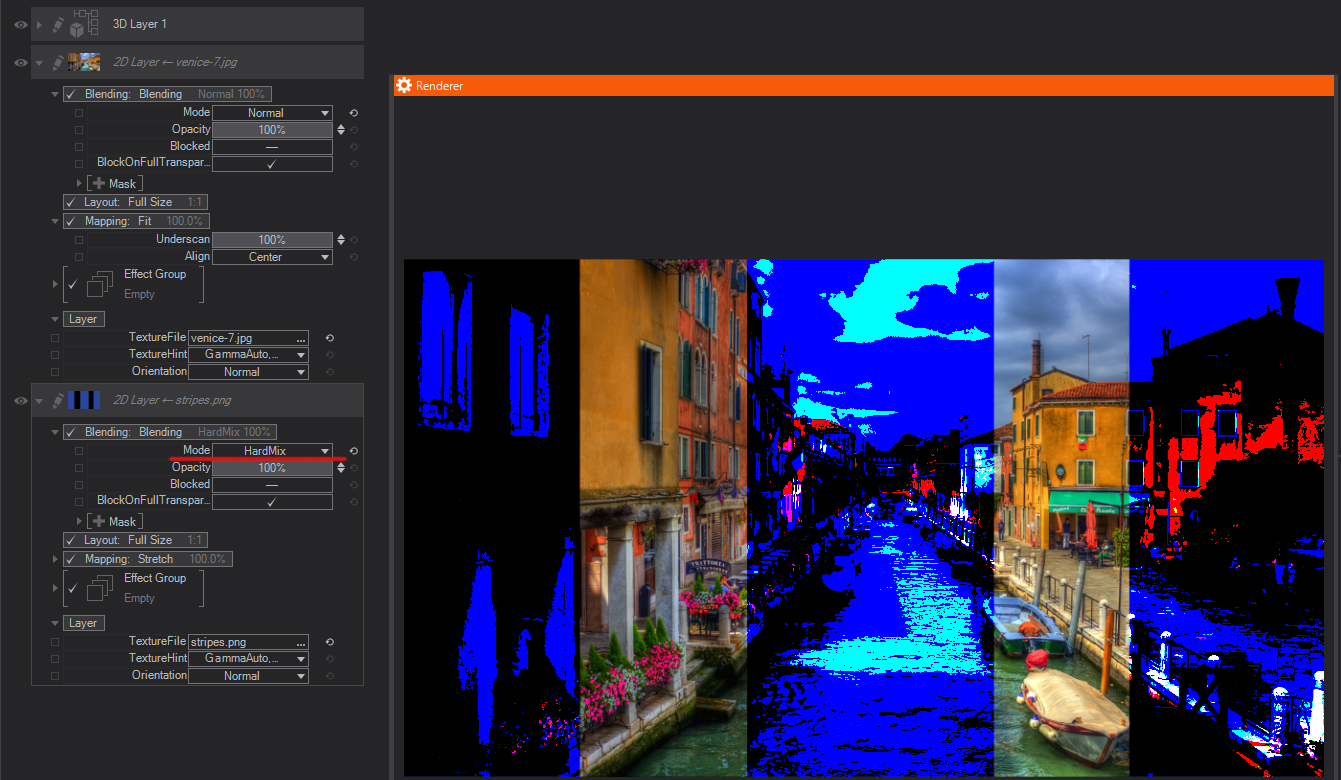
Hard Mix: Adds the red, green and blue channel values of the blend color to the RGB values of the base color. If the resulting sum for a channel is 255 or greater, it receives a value of 255; if less than 255, a value of 0. Therefore, all blended pixels have red, green, and blue channel values of either 0 or 255. This changes all pixels to primary additive colors (red, green, or blue), white, or black.
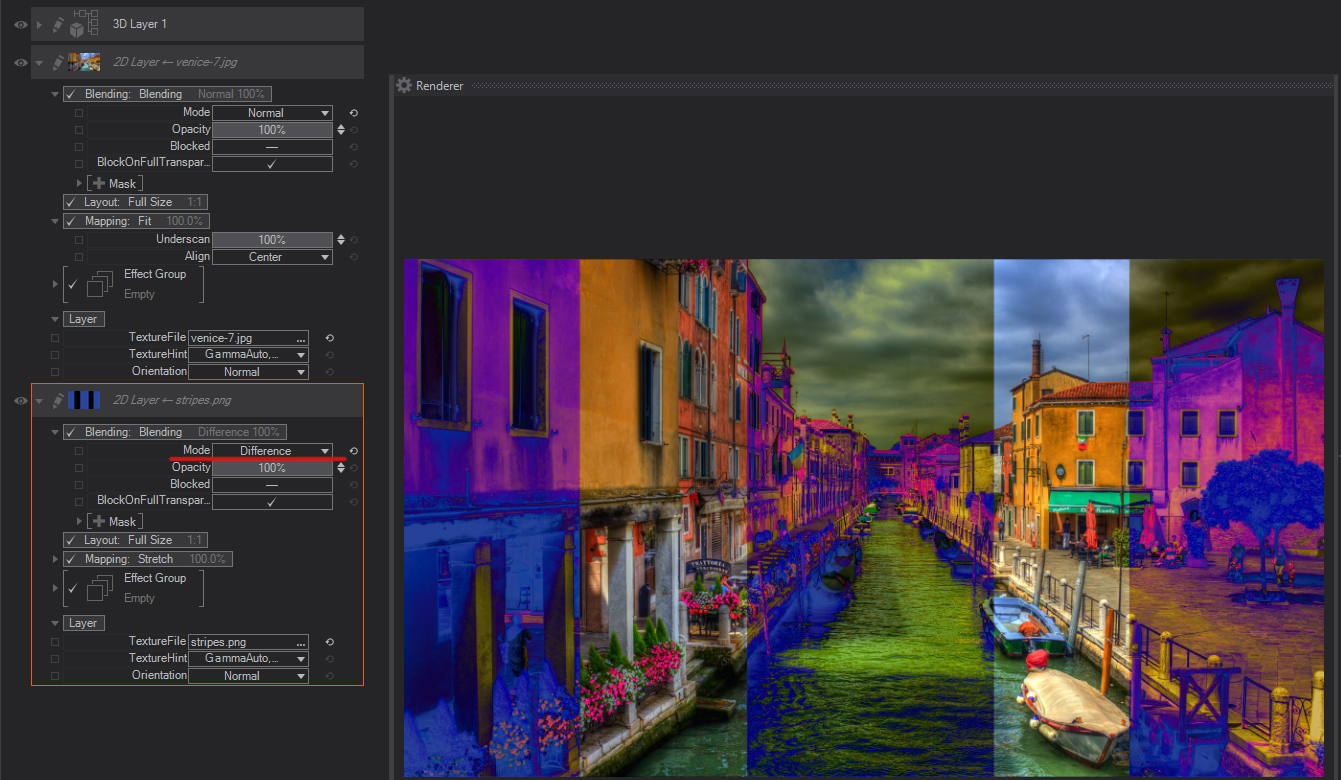
Difference: Looks at the color information in each channel and subtracts either the blend color from the base color or the base color from the blend color, depending on which has the greater brightness value. Blending with white inverts the base color values; blending with black produces no change.
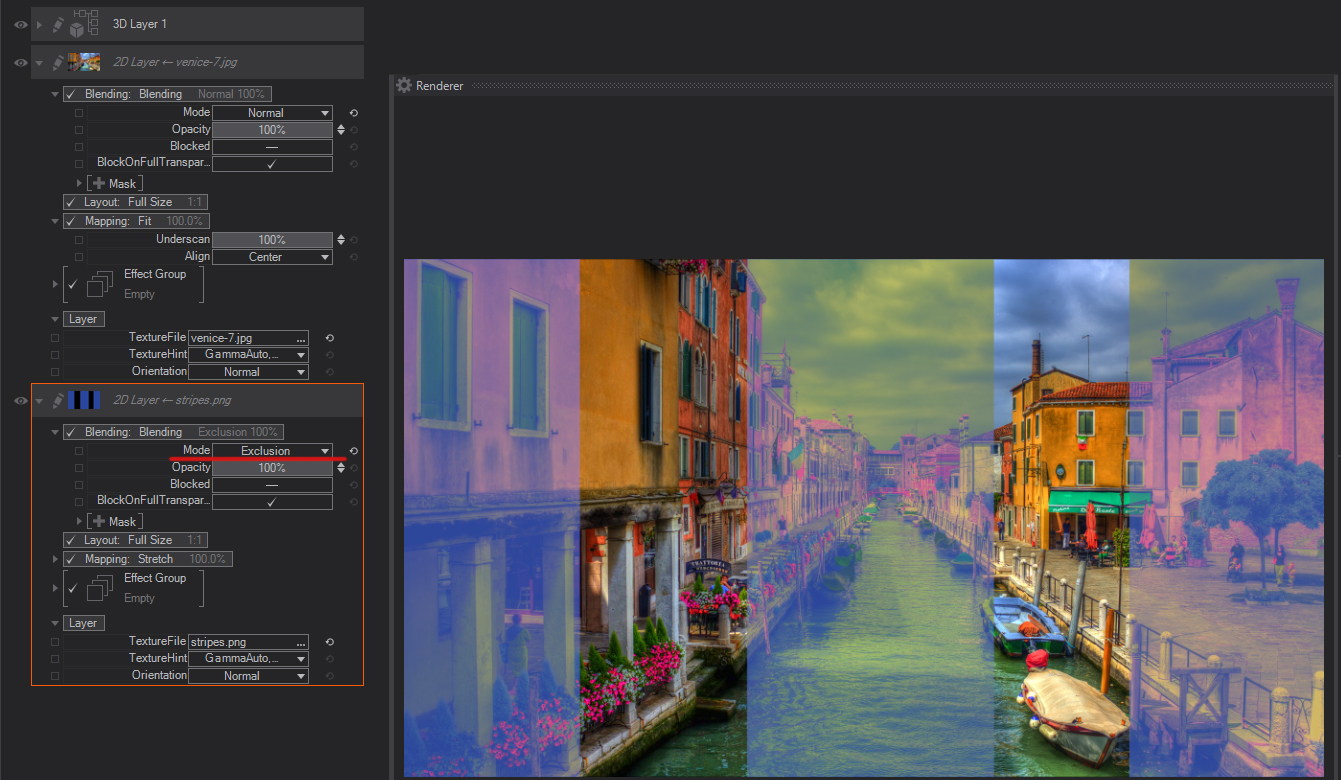
Exclusion: Creates an effect similar to but lower in contrast than the Difference mode. Blending with white inverts the base color values. Blending with black produces no change.
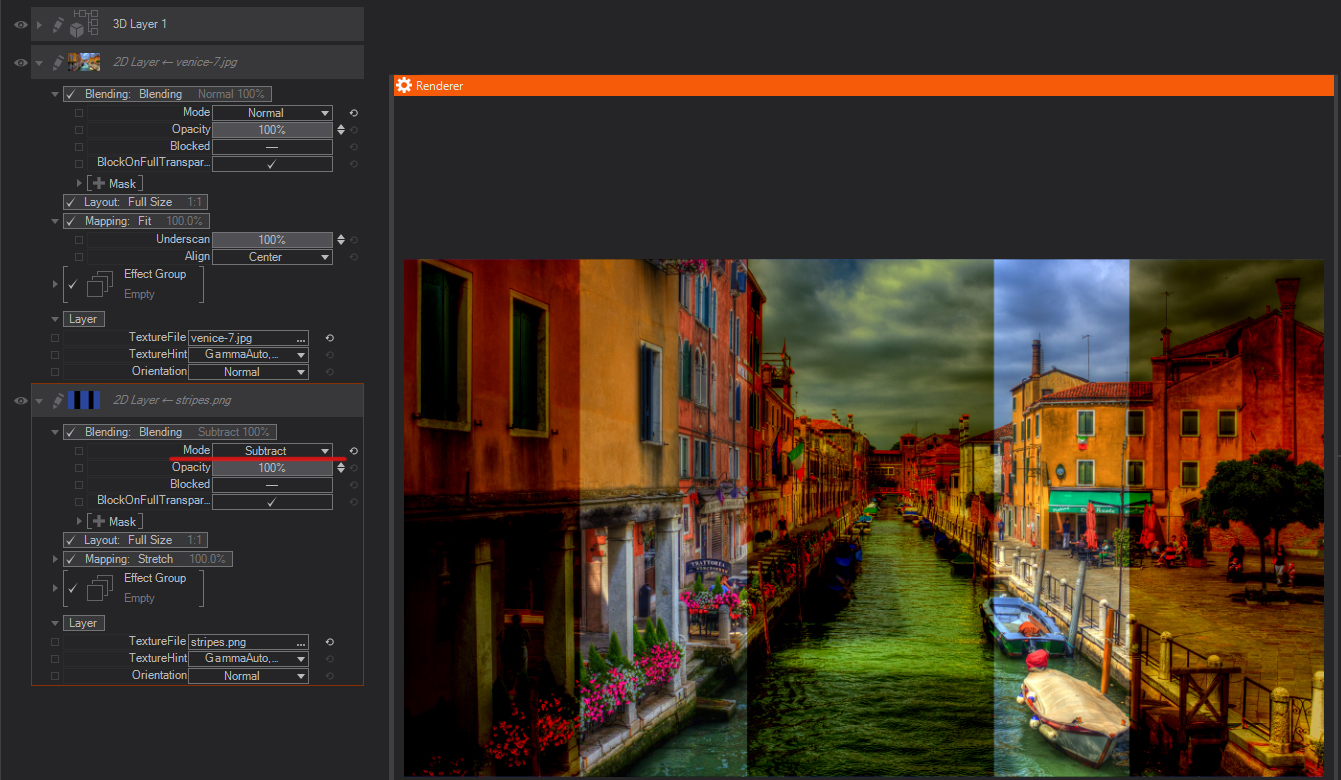
Subtract: Looks at the color information in each channel and subtracts the blend color from the base color. In 8- and 16-bit images, any resulting negative values are clipped to zero.
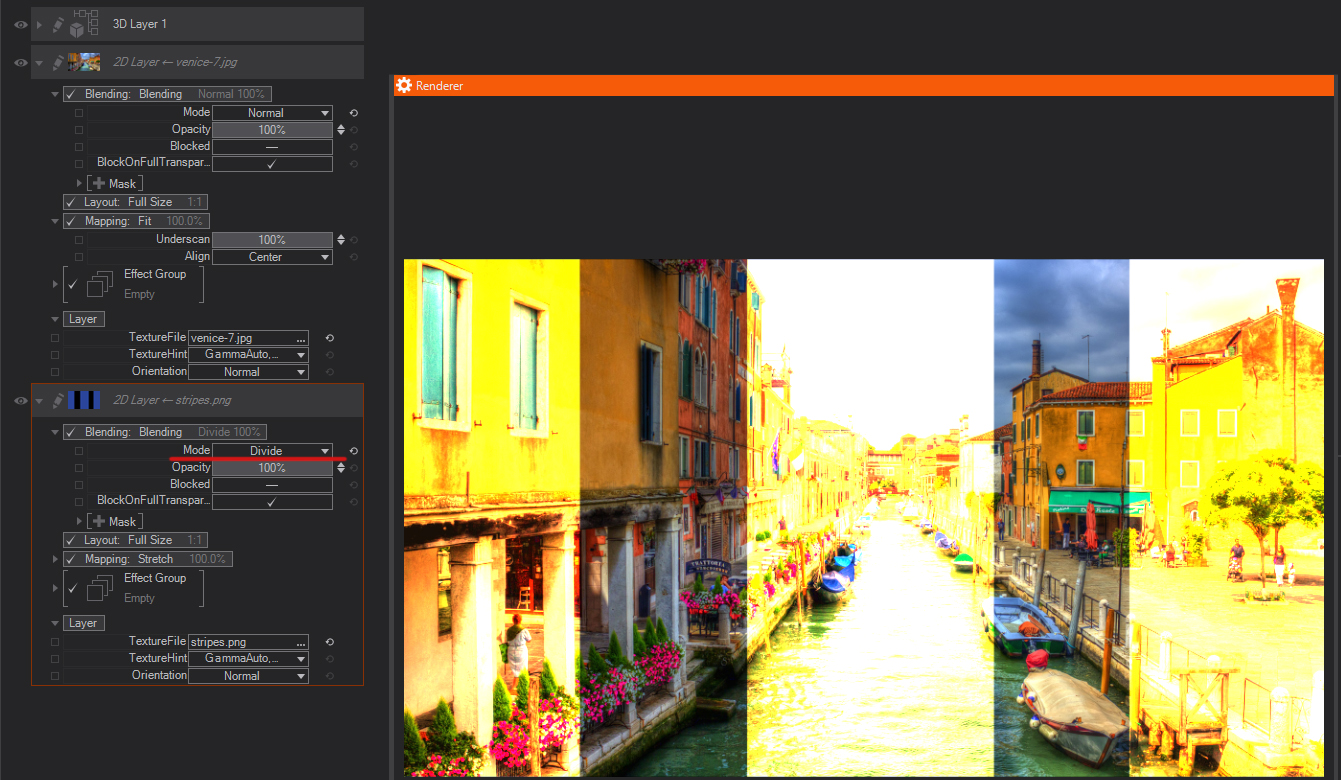
Divide: Looks at the color information in each channel and divides the blend color from the base color.
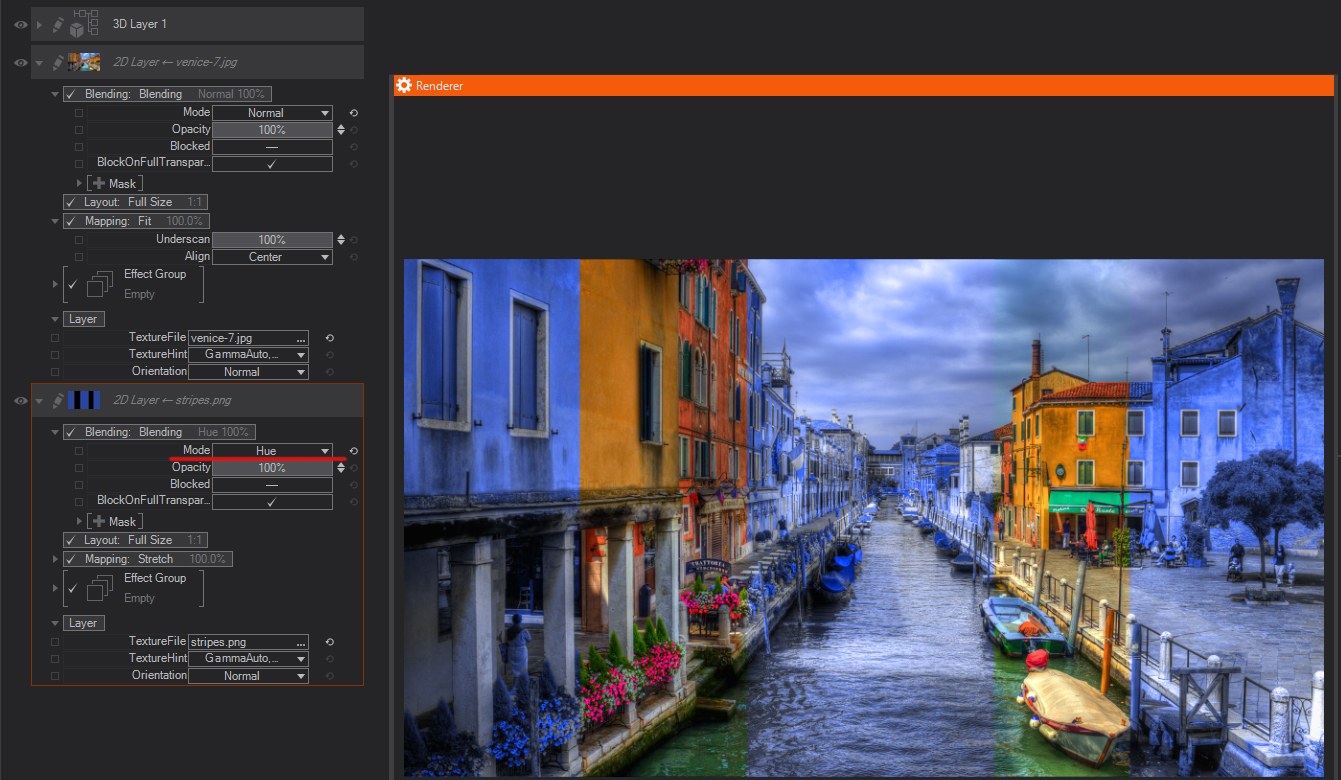
Hue: Keeps the Hue of the layer, and blends the luminance and saturation of the underlying layers (you basically get the image from the lower layer with the colors of the top layer).
Saturation: Keeps the saturation of the layer, and blends the luminosity and hue from the underlying layers—where colors from the active layer are saturated, they will appear using the luminosity and hue from the underlying layers.
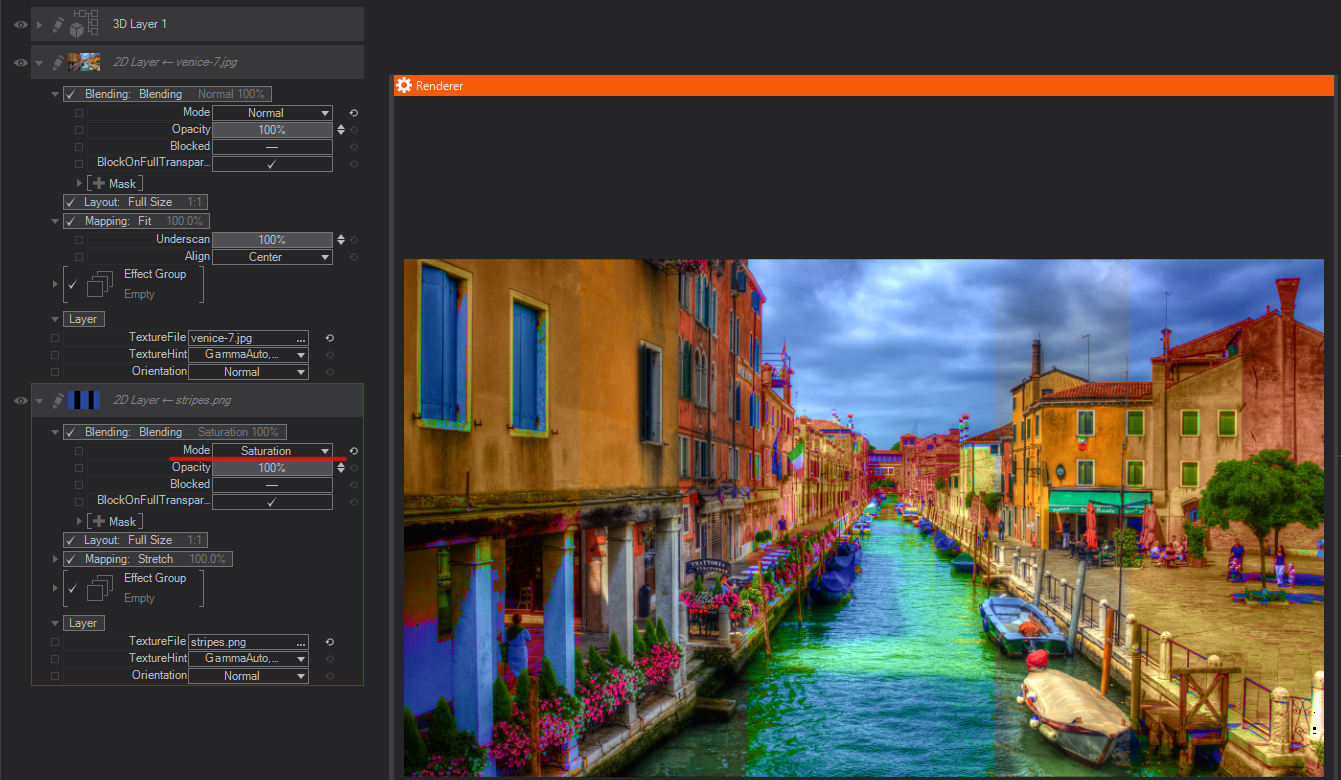
Color: Keeps the color of the layer, and blends the hue and saturation (the color) of the active layer with the luminance of the lower layers.
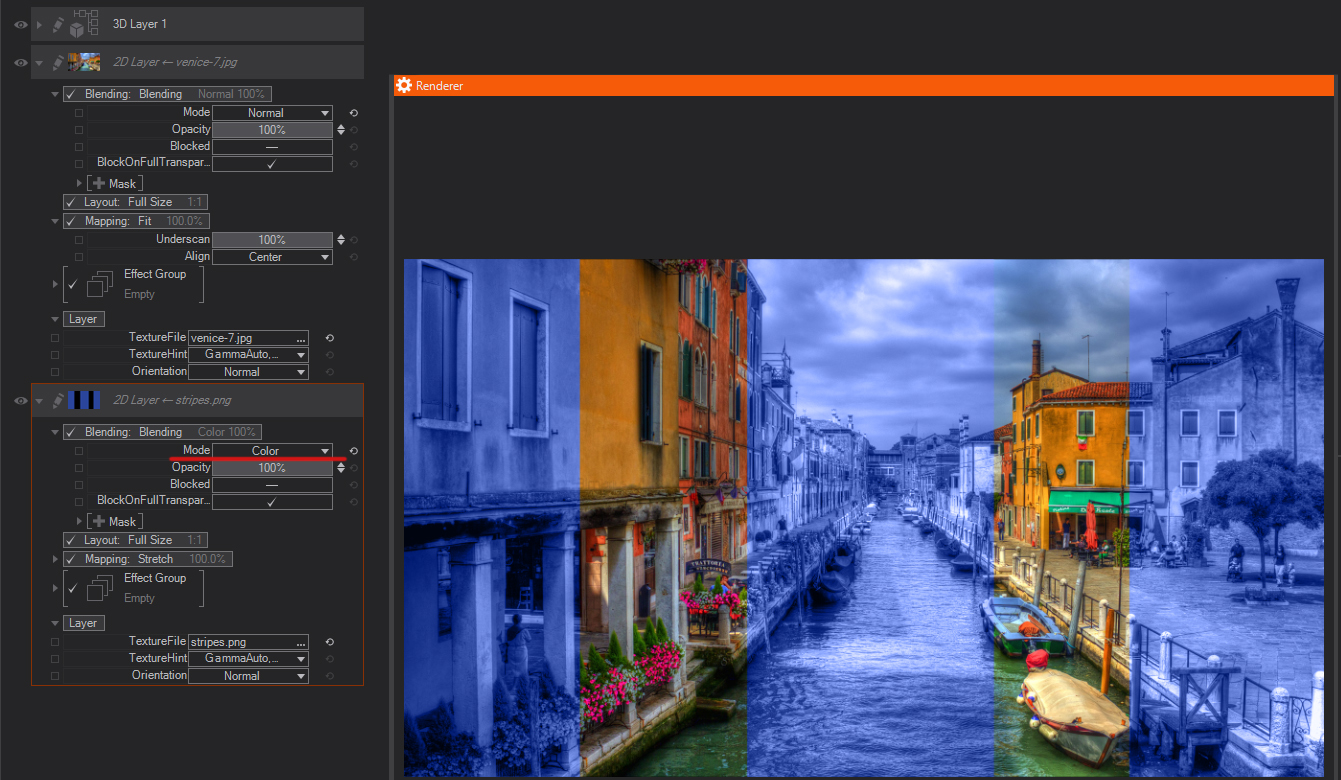
Luminosity: Keeps the luminance of the layer, and blends it with hue and saturation of the layers below.
Linear Light: Uses a combination of the Linear Dodge blend mode on the lighter pixels, and the Linear Burn blend mode on the darker pixels.
Pass Through: Is the default Blend Mode for Layer Groups. It allows any adjustments to layers inside the group to affect layers below it. Ventuz takes all the layers inside the Group and performs the blending operations in the usual order - if you change this mode you are basically changing the order in which the layers are processed - all layers inside the group are blended first and the resulting composite is blended with the layers below with the selected blending mode for the group.
Blend mode Pass Trough applies only to Layer Groups!
Texture is not pre-multiplied: This setting forces an internal pre-multiplication of textures in certain image formats, mainly DDS when it is difficult to automatically decide if the file is pre-multiplied or not.
Opacity
Control the overall Opacity of the Layer. This value is already exposed to the Layer Level.
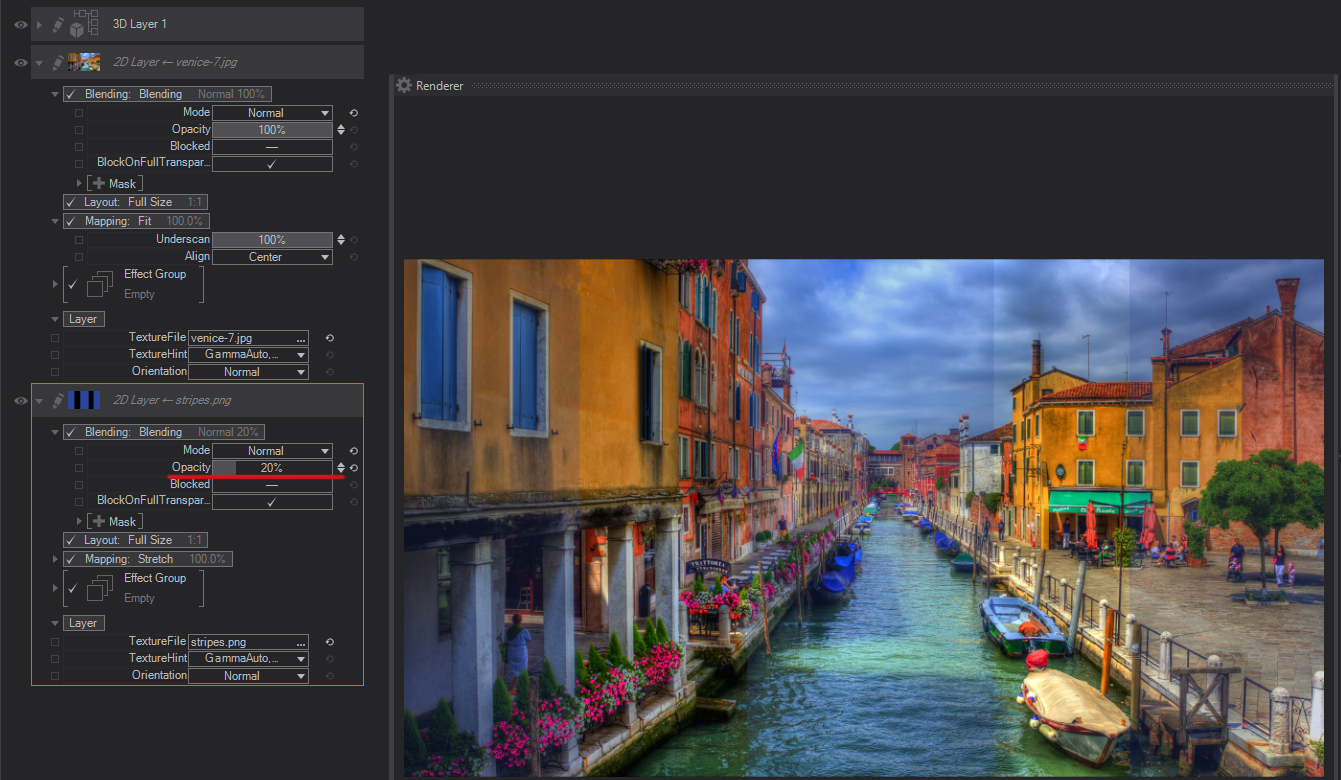
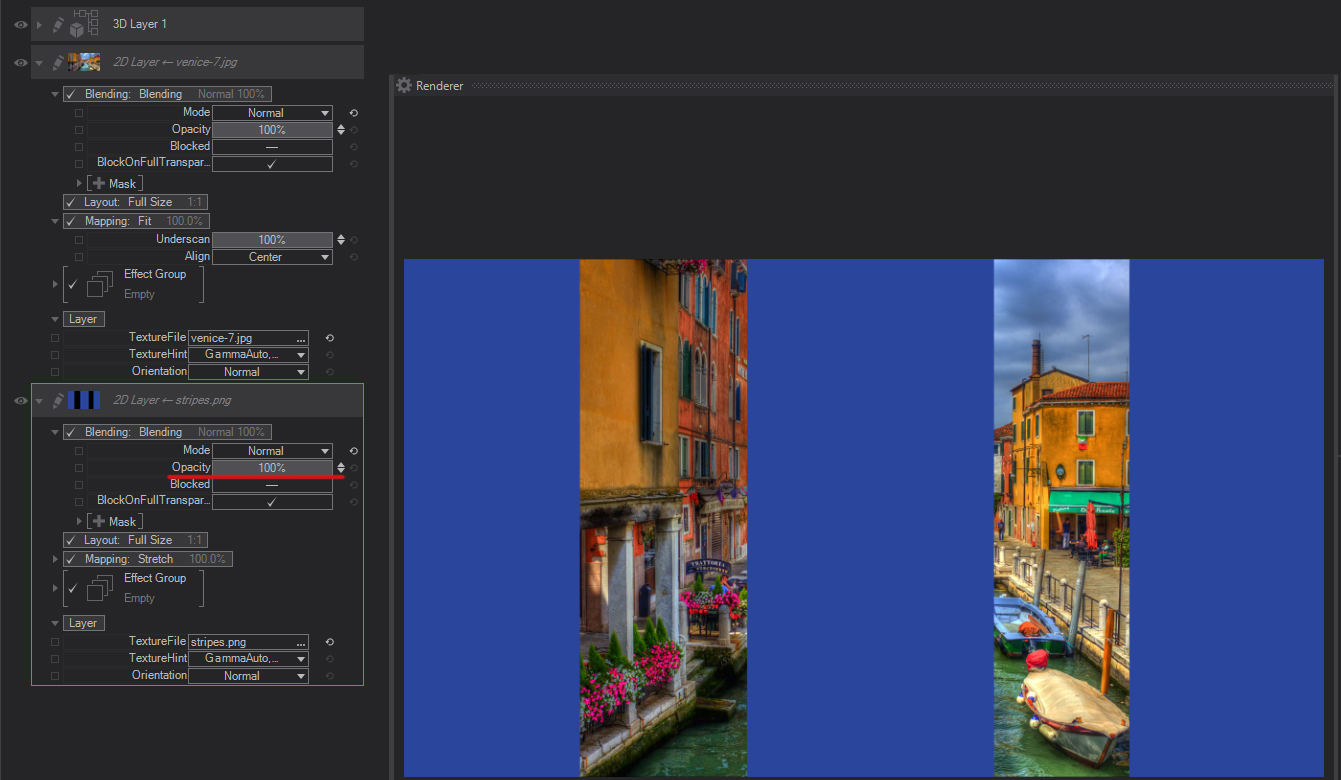
Blocked
This checkbox controls if the Layer Blending mode operation is performed or not, the main difference with switching OFF Blending operations is that the property can be bound in the Content Editor, and therefore can be used to optimize performance in complex scenes.
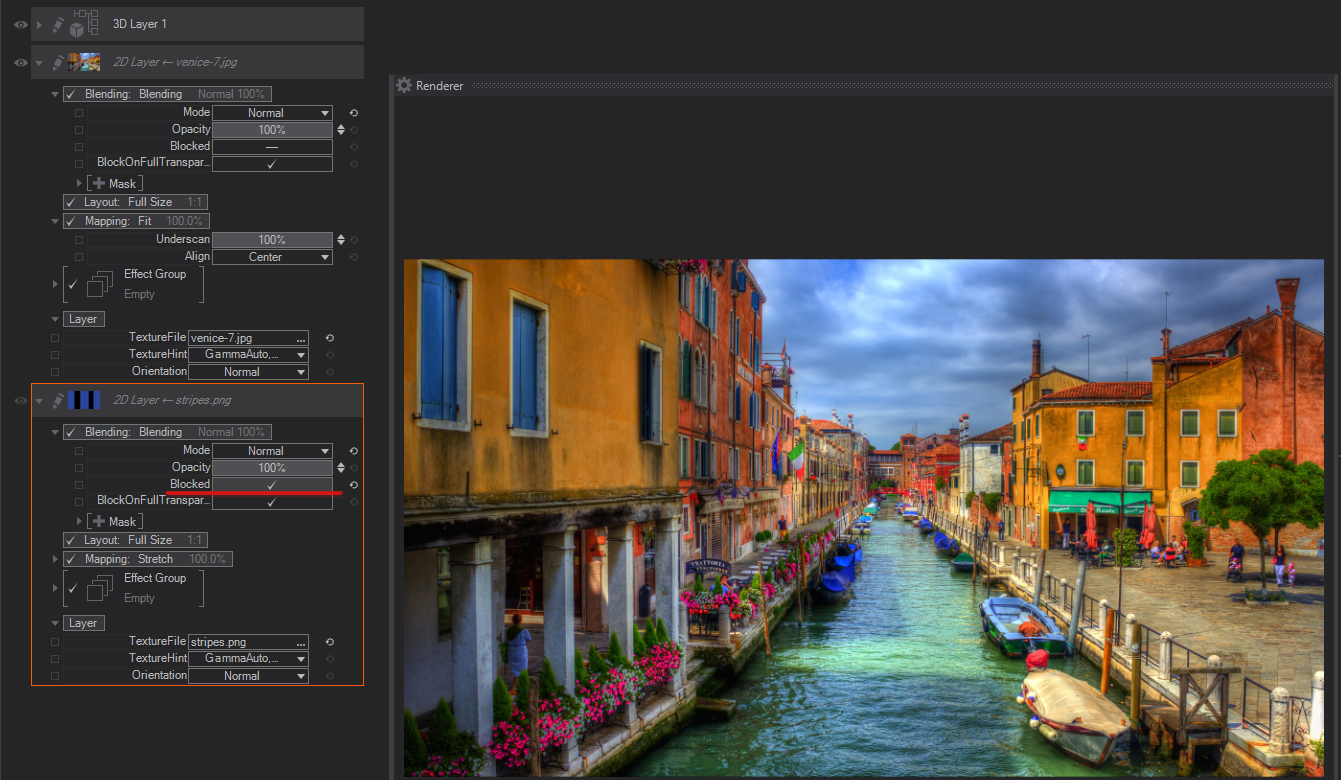
BlockedOnFullTransparency
This checkbox is used to optimize layer performance when animating Layer Opacity, if opacity is set to 0%, and is, therefore, invisible, Ventuz will minimize any calculations pertaining to this layer to improve performance. If you Uncheck BlockedOnFullTransparency to still have touch interactions possible. For instance, you could have a Transparent 2D Layer which shrunk in size and can still send touch information.
Layer Mask
Layer Masks allow isolating certain parts of the layer to be used for the final composite. In general, Masks use the color or alpha information to decide which image pixels will be transparent, translucent or opaque.
- Pixels which are 100% white in the selected channel will result in opaque areas of the layer.
- On the contrary, pixels which are 100% black in the selected mask channel will be considered as transparent and therefore these areas of the current layer won't be shown in the final composite.
- All the gray tones between black and white in the selected mask channel will result in different levels of translucency in the areas affected.
Ventuz features three type of masks by default: Mask, Vignette and Border. You can add as many MaskStages as you want.
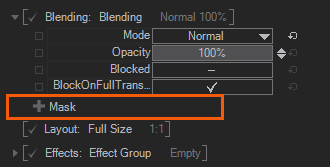
You add a LayerMask if you click Click on the [+] Mask like shown on the Screenshot, and select Mask or any type of Mask Vignette / Mask Border from the dropdown menu.
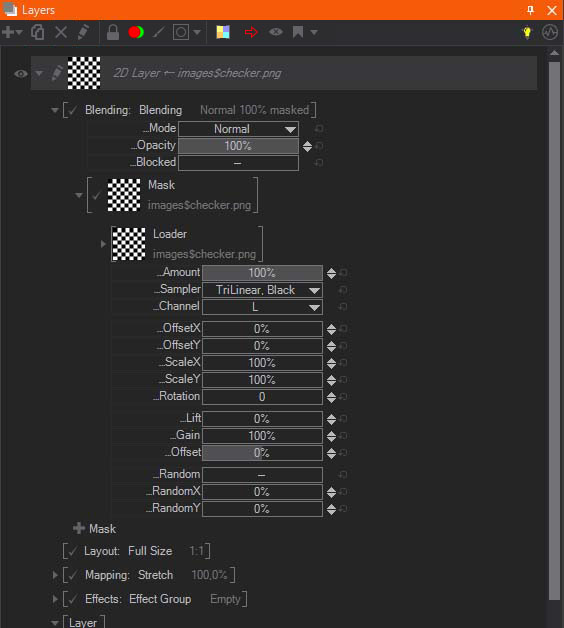
Mask
Mask Property uses a texture source as the mask. When adding a mask, a new thumbnail will show the Mask appearance. Click on the Mask or click the triangle in the front to bring up the properties for the selected Layer Mask.
Each one of the Texture Source property groups provide a texture to the containing node that is used in one way or another. This page gives an overview of the different types of property groups.
Texture Loader
The Texture Loader directly loads a texture of any supported type from file and provides it as a texture to the containing node. The File property changes the loaded image. The Hint property will change how the loaded file is handled internally while the texture is generated. See Texture Loader Node for more information on the Gamma and Alpha Hints used when loading a texture.
The Presets of this Node are specific internal Texture Files that are always available in the Ventuz Runtime.
These images can be used for several different general purposes like generic textures or placeholder and testing.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| ||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| ||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
These images are intended to be used by Ventuz' Image Post Processing Effects, e.g. the Lensflare effect.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| ||||
These images are best used by texture based Lighting Models and specific shaders, like e.g. the Incidence Lighting Model or the Hatch Texture Node.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| ||||
Texture Property
The Texture Property Property Group provides only an Input for any Texture coming from the scenes logic, e.g. a Texture Loader Node. This is necessary for some source types like movies but may also be useful whenever you need to apply some logic to loaded textures before applying them to objects. The Presets generate the according Content Node together with the Property Group and bind its Input Property to that new node.
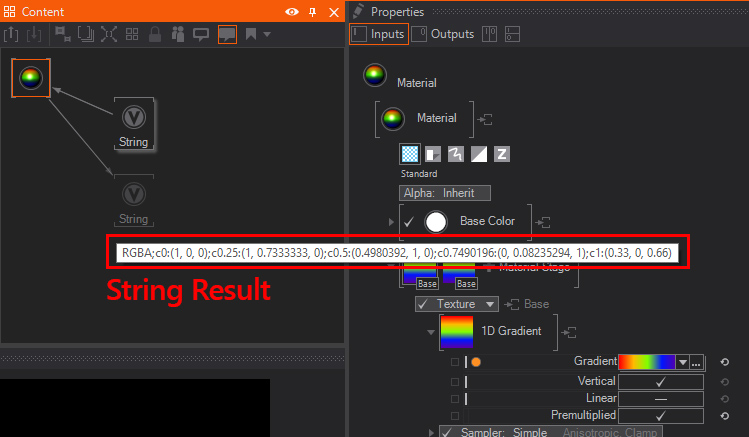
1D Gradient
The 1D Gradient generates a linear gradient. It can be edited using the Gradient Input - clicking on the down arrow on the left of the property will open up the Gradient Editor. The Vertical flag changes the alignment of the generated 1D gradient. You can also use a String node to Copy&Paste gradients from or into a gradient property, simply bind the
These are presets for the Gradient Generators. Instead of files these are represented as strings and as such can be bound to the input of a Gradient Property.
|
|
| Image/Texture |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
SVG Loader and SVG Text
The SVG Loader and SVG Text Property Groups rasterize an SVG file and provide the rasterized graphic. See the SVG Loader Node for more information.
The images in this category are defaults for other kinds of texture usages, like the rasterization of SVG Files.
|
|
|
|
| |
Mask Properties
For any of the above loaders, you can adjust the Amount which controls the Mask Opacity, the Sampler where you can select the filtering to be Trilinear and Adress the Border behavior. Click the Sampler and the Dropdown Menu offers you following Options for the Border Behavior:
Black: The pixels outside the area covered by the mask are turned black, meaning that there is no tiling.
White: The pixels outside the area covered by the mask are turned white, meaning that the area outside the original mask image is totally opaque.
Clamp: The pixels outside the area covered by the mask will repeat endlessly the same values as the pixels in the original image borders.
Wrap: The pixels outside the area covered by the mask are repeated or tiled as they were in the original mask image.
Mirror: The pixels outside the area covered by the mask are repeated or tiled as they were in the original mask image, but inverted like a mirror effect.
With the Channel Drop Down Menu you can select which channel should be taken for masking. The Luma (L) is the default and uses the external image Luminance as a mask, it converts the image internally into a Grayscale Image. You can select an explicit channel like R,G,B or take the Alpha as the Making source. With the Invert the source image or selected channel gets inverted.
You can Offset X/Y, Scale X/Y and change the Rotation of the mask. New pixel values are interpolated using the options selected in the Sampler dropdown menu.
The Lift, Gain and Offset can be used to do a color grading for the Mask. The values are conformed with the Standards used in the cinematography. Lift can lift up the lower colors, while it clamps also the lower color area. E.g. if you lift a dark image, lower colors gets cut off, instead of starting at 0-255, it will start with 30-255. Gain boosts the colors in the whole range, while bright pixels may also clip at 255. Offset moves the colors in respect to each other color values. It behaves like a shifting.
Random will position the Image randomly on screen and the amount of this randomness can be controlled with the Random X/Y. The Image will be positioned to a different position for every Tick, therefore you can not control the speed.
Mask Vignette
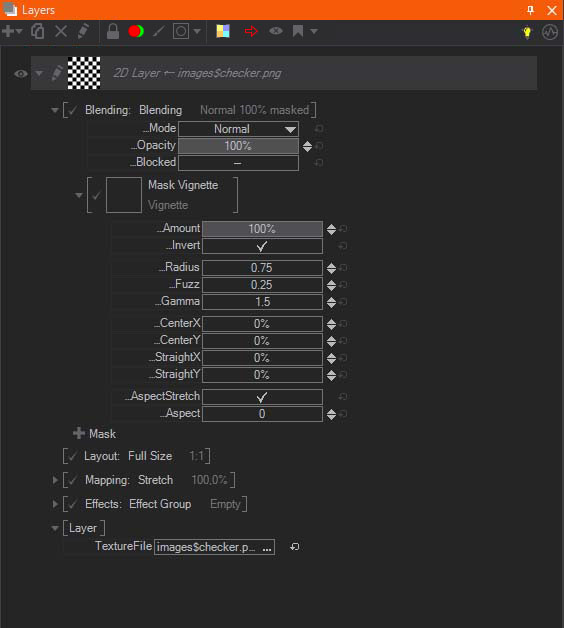
Mask Vignette can be used to darken the corners of the Layer. You can control the Radius and Fuzz to change the appearance of the vignette. Fuzz will change the blending between the dark vignette and the visible area. You can reposition with the Center X/Y values and also use Straight X/Y to change the shape of the vignette. The Straight can be used to shape the circle like vignette to a rounded rectangular shape. With the AspectStretch and Aspect value you squeeze or stretch the vignette.
Horizontal Vignette and Vertical Vignette offer the same controls as the Standard Mask. They are more like presets and have just the properties adjusted, so that either a Horizontal- or Vertical Vignette appears. The adjusted Values, in this case, are Radius, Fuzz and depending on Straight X or Straight Y.
Mask Border
Mask Border creates a rectangular border vignette which can be controlled and adjusted the same way as the Standard Vignette. The main difference is the Border X/Y controls. These control the border width. You will notice that you control the rounding of the border with the Radius value.
Round 2% and Square 2% are again just like presets, which have the Border X/Y set at 2% and either Radius and Fuzz set at a value or not.
Layout
The Layout parameters adjust the layer size, aspect and position. The layout can work in different ways, also called modes, each features its own properties.
Full Size keeps the Layer size always to the project settings. Switch to the Percentage if you want to adjust the Layer Size and Position in percent. For example: This mode is the fastest way to bring a Layer on-screen and off-screen, since you just need to bind the X/Y values, and animate them.
Pixels will switch the layer to be pixel accurate. Per default, it will use the Project Settings. If you started your Project in FullHD it will reflect 1920x1080. The X/Y changes the on-screen position in Pixels, keep in mind that the position is dependent on the Relation Alignment. As soon as you change the Width/Height the layer will have the set size. In the Relation dropdown you can define in which relation the pixel will be. The Relation - Layer will use the pixelspace defined in the layer itself OR if the layer is inside a Layer Group and the Layer Group has a different pixelspace it will be in relation to that Layer Group settings. Relation - Project will use the defined Format of the Project Settings. E.g. your screen is set to 1920x1080 and you resize the Renderer View the layer will still render as if it will be displayed in FullHD. Resizing the Renderer View will not affect the displayed size of your content in this case. With the Relation - Alignment settings you change the alignment of your layer which also affects the positioning values.
Aspect can be used to redefine the aspect of the Layer independently of the Format which you set in the Project Properties.
Offscreen Render Target renders the whole layer to an internal texture which you can access in the Layer - Output Properties. With the Size dropdown menu you can choose if you want to render the layer internally in Full- Half- or Quater- size. For example a 1920x1080px Layer will be 960x540px if you select Half size here. You can also adjust the internal size manually (Manual). Ventuz has some Presets, e.g. 256x256, 512x512, 1024x1024px ..., and so on. As soon as you select any manual size, you can change these values with the Width/Height to suit your needs. Per default the RenderMode is set to Always which renders the Offscreen Render Target in every frame, you can switch to Render Once, so that the Offscreen Render Target is rendered only one time. You can trigger the RenderNow to have the Offscreen Render Target rendered again. The TouchEnabled property specifies if this Layer should be taken into account by the Touch Input Processing. The only Option left is the MipMaps. If enabled the Layer will automatically create MipMaps from its texture. It consumes some performance but will enhance the quality of the Layer if scaled down.
Mapping
The Mapping parameters only appear on 2D layers.
The Mapping parameters are used to edit how the texture is mapped onto the Layer. Ventuz supports various Mapping modes, each one featuring its own parameters to control the texture position, size tiling, etc..
Stretch will stretch the Texture Aspect ratio to match the layer surface Aspect ratio, hence deforming the textures original proportions. With the Underscan you scale up the texture, but keeping the texture stretched to fully cover the layer and its proportions.
Fit you scales the Texture to match the maximum bounds while keeping the aspect ratio of the original and creating a letterbox or column where there is no image. Align adds control for the texture alignment.
Crop will scale the texture to match the minimum bounds, while keeping the original aspect ratio, cutting off any part of the image that is out of bounds.
Extended allows for external logic to determine the mapping, allowing for dynamic adjustment as required during runtime. It can perform as Stretch, Fit or Crop. You change the Extended Mode with the SizeMode dropdown menu. Tiles mapping type controls how textures are repeated when they are smaller than the layer. The tiles can be fully adjusted with CenterX/Y, Scale All and Rotate. The Shear X/Y values. You can stretch the texture in both directions of the same axis at once, hence making it look like it's been sheared. When Mirror is selected the texture will be mirrored in all axis or sides instead of repeated.
Polar will cause the horizontal direction to be mapped to a circular direction. For example, a straight line across the middle becomes a circle. It is very useful when creating and working with certain graphical effects.
Smaller Amount values will divide the other Polar Distortion parameters, meaning that smaller values will interpolate between the original image and the Polar Distortion effect– this is great for animating the Polar Distortion effect as a whole. With the Inverse you toggle to control which coordinate system conversion is applied. If the default Off value is selected the effect will convert from standard Cartesian X,Y to Polar coordinate system, like the "Rect to Polar" setting in other software packages on the market. The Center X/Y values move the center of the Polar Distortion effect calculation. The units are expressed as Percentage of total Image resolution. You can Scale X/Y axis individually and/or Scale All as a whole. The Segments control a number of segments iterations created. With the Radial Scale you control the result according to the Polar coordinate system with higher values stretching pixel positions in polar directions from the Center location, while smaller values will shrink towards the center location. The Swirl is to deform the Polar Distortion as a spiral, in other words, the higher the values, the more complex the spiral created by the Polar Distortion. Scroll X/Y move the Polar Distortion segments radially in the polar X and Y axis individually. The Perspective setting forces the Polar Distortion effect to try to mimic a fake perspective - it is useful to simulate Tunnel-like effects. If you enabled the Perspective you can use Perspective Adjust and it works like if you would adjust the FOV of the perspective. The Aspect Stretch can be used to apply stretching to the Image. If turned on the Aspect is used to control the Aspect ratio or proportions of the distortion.
Kaleidoscope mimics the illusion of an optical toy for producing symmetrical patterns by multiple reflections in inclined mirrors inside a tube. This technique is primarily used for creating graphical background effects and animations.
You can relocate the Center X/Y for the Kaleidoscope, Scale X/Y and Scale All. With the Segments you change the number of instances of the original image created internally and duplicated along the polar coordinates. The Radial Scale changes the scale of the segments in the radial direction, meaning the number of segment levels to create the final kaleidoscope effect. With Bulge you apply a bulge like deformation at the center of the Kaleidoscope, meaning that kaleidoscope will be distorted radially from the center, a new level will be generated according to the values. With negative values, it will keep expanding the center deformation and positive values will compress to the deformation center. You can Rotate which works like if you would rotate the Kaleidoscope Tube. Rotate in Segments will rotate the Kaleidoscope individually, in other words, each segment will be rotated around its own rotation center. The Swirl is to deform the Kaleidoscope as a spiral, the higher the values, the more complex the spiral created by the Kaleidoscope will be - negative values work the same, just turning the spiral in the opposite direction. Scroll X/Y will move the Kaleidoscope segments radially in the polar X and Y axis individually. Toggle Perspective to activate the Perspective calculation. When turned on the Perspective Adjust can be used to control the Perspective calculation. The Aspect Stretch can be used to apply stretching to the Image. If turned on the Aspect is used to control the Aspect ratio or proportions of the Kaleidoscope.
Effects
For every layer, you can apply different kinds of effects. You can Group effects by creating Effect Groups and assigning individual Blendings and Masks.
Margin will be mostly required if you apply the dropshadow or blur effect. The Margin, which is expressed in percentage relative to the original layer size, adds a border around a nonfull-size layer. That is especially required for effects that affect a greater area than the layer itself.
Blending
Uses the same available modes like for the layer blend modes. Please see Blending modes for layers.
Mask
Uses the same available masks like for the layer masks - the exception is the additional mask self-property. Please see the Layer Masks for an overall detailed explanation.
Mask Self masks the applied effect using the Layer Color information. It renders the effect and applies the Layer itself on top of it. This can be greatly seen with the Crashzoom effect and enabled Mask Self:

If you enable the Show Effect, you will see only the effect and the applied Mask Self is ignored then.
Effect
Click the [+] Effect and add any of the effects listed below. Keep in mind that you can Group Effects! You can change the order of the effect or effect group the same way like you would do with the mask layers - simply click the arrow next to the fx stage or the cross to delete it.
For effect stages you can clone or clone with bindings.To do so Hold Right Click Hold on an effect stage for a second and a menu with these options will show up.
You can collapse or unfold effect properties by simply Right Click click an effect stage.
Effect Group
Creates a group of effects that will be applied together at once. It works exactly the same as the Effects Stack, so the same Effects can be added, moved, deleted and enabled inside of the Group in the same way you operate with the Effects Stack.
Color Correction
These effects are used to correct the color values of the layer. The available Color Correction IPP Effects are Grayscale (simple Grayscale effect), Color Grading (a standard color correction effect working with the RGB primaries), Color Correction (similar to Color Grading, but using the HSL/HSV Color model), Gain (quick Gain color correction effect), Tone Mapping (applies tone mapping curves), LUT (applies a LUT as effect on the Layer)
Please refer to the IPP Color Correction Effects section of the User Manual for additional information.
Filters
These effects filter the pixel values of each layer, changing their position, adding new elements, or even changing the opacity.
The available Filter IPP Effects are:
Mosaic: Creates a set of tiles colored according to the original color values.
Blur: Averages each pixel color values with the surrounding pixel values.
Glare : Creates a smooth halo around the brightest areas of the layer.
Crash Zoom: Is often called "God Rays".
RGB Noise: Adds a video noise-like effect.
Feedback : Creates a trail effect by blending with previous frames.
Posterize RGB: Rounds up/down pixel color values.
Posterize HSV: Posterize effect based on the HSV color mode.
Edge Detection: Detects the outline of shapes in the Layer.
Color Difference Keyer: Used to Key out the green from "green-screen material" - similar to a Chroma Keyer but uses different math.
Please refer to the IPP Filter Effects section of the User Manual for additional information.
Distortion
These IPP Effects work mostly by changing the relative position of pixels in the layer.
The available Filter IPP Effects are:
Drop Shadow: 2D shadow effect based on Layer Alpha.
Lens Distortion: Replicates artifacts created by lens spatial aberrations.
Distortion: A standard distortion effect, combining most of the options available in the rest of IPP distortion effects.
RGB Distortion: Offsets and scales Layer RGB channels individually.
2D Displacement: Displaces the Layer pixels according to the Luminance information of an external file.
Noise Distortion: Uses a randomly animated texture to create a fake Noise Displacement effect.
Polar Distortion: Transposes the x and Y pixel coordinates in the original image to a Polar Coordinate system.
Kaleidoscope Distortion: Kaleidoscope pattern effect.
Please refer to the IPP Distortion Effects section of the User Manual for an overall detailed description.
Layer
These Properties may vary for the different Layer-types. The most common Property is the Orientation Property which makes it possible to Rotate the Layer in any direction or Mirror and Flip it. There are several Layer-specific properties depending on the Layer Type. The Image Layer has Properties like the TextureFile and TextureHint which controls the Gamma and Alpha loading, while for example the Constant Color Layer has a TextureColor Property. As mentioned before, each Layer Type may vary in the Layer Properties.
One important property to mention is the RenderFilter. You can chose here to have set All which is the default or explicitly set any of the available filter channels from A - H.
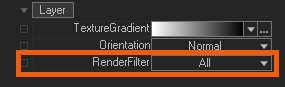
You can use these filter flags to have the Layer filtered from being shown on the given output. You can select on the Render Setup Editor in the outputs properties to have a RenderFilter applied - its the same range from A - H.