Color Management and HDR Workflow
Table of Contents
Introduction
Ventuz 8 introduces a full color management workflow with HDR capapbility and different wide color spaces, from the incoming video file to individual output streams. Especially with the usage of modern LED-panels technology, the production can be elevated with the full range of dynamics and a sophisticated color management.
Overview
What is different in linear Color Spaces?
The main change for the engine is to calculate color values with 16-bit float values, instead of 8-bit integer. Even though this seems like a background technical change, this enables Ventuz to work with a non-fixed dynamic range while still achieving high precision. Processes like PBR material and light rendering greatly benefit from this unbound dynamic range. This is also the foundation for the color processing of input and output video.
It is very recommended to read the background information about Color Spaces to work properly with HDR and color spaces.
With color processing for the whole rendering pipe, Ventuz ensures that an incoming video in a specific color space renders color-accurately on the output, where the rendering color space is independent of the output device's color space.
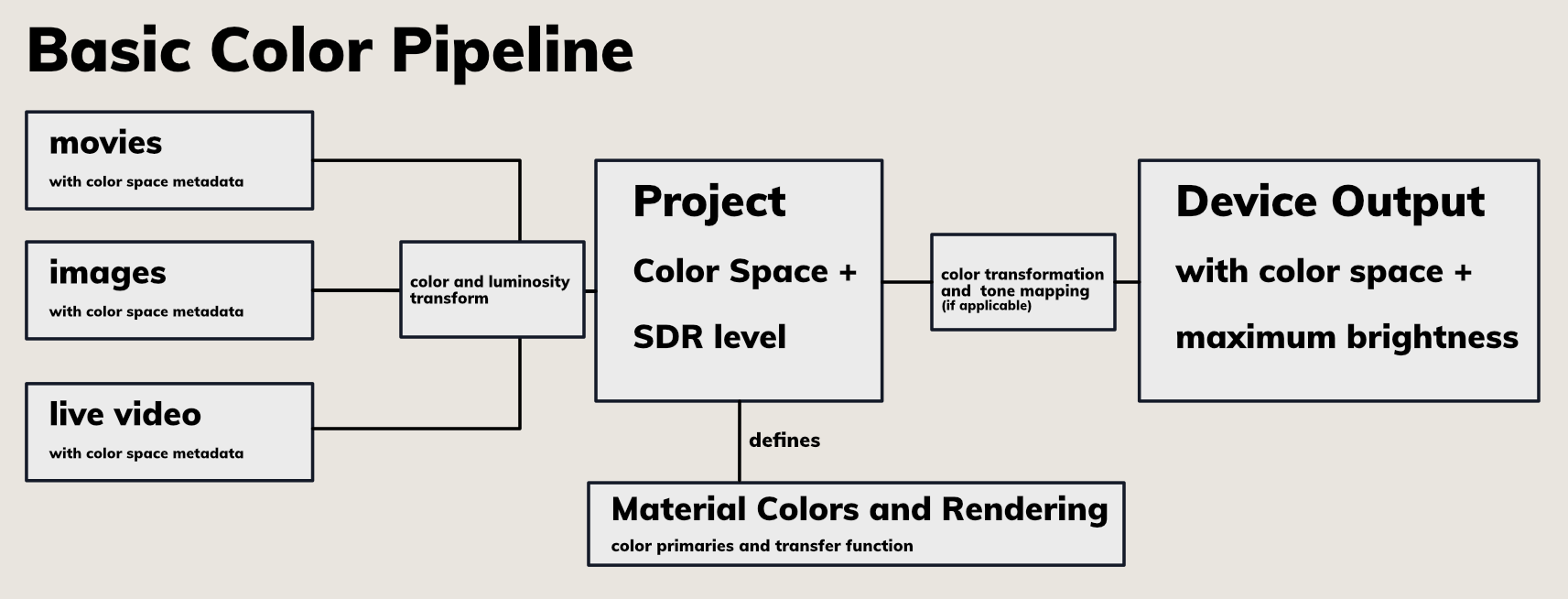
Ventuz auto-detects the color space and other meta-data for all incoming and outgoing video streams and applies the correct color transforms in real-time, to ensure a workflow with minimal additional configuration. In general, all incoming video will be converted to the Project's Color Space. On the device output, the video stream is color transformed again to match the output device independently per Output. For specific use-cases, all of these transforms can be manually adjusted.
Technical Setup
To enable rendering for HDR in linear color spaces, please follow this How To Enable Linear Color Spaces and HDR Video Output
A short checklist for HDR:
☐ HDR capable output device.
☐ Activate HDR in Windows settings.
- Soth of these settings are necessary to view and playout via the GPU in HDR.
☐ Set Project Color Space to a linear color space.
- Sets the engine to 16-bit float calculation.
Working with Color Spaces in Ventuz
Standard Rendering
When the Project's Color Space set to the default Rec.709/sRGB, the engine behaves exactly like pre Ventuz 8. Existing Projects will look the same. If there is no need for HDR capabilities or specific color management in your existing project, it is recommended to leave the Project Color Space set to its default Rec.709/sRGB. Across this documentation we call this the SDR Workflow. An advantage of the standard workflow is a sligthly better rendering performance, with its 8-bit calculation.
Linear Color Spaces
There are some considerations that should be taken into account when deciding to work in a linear HDR capable color space. First, the capability of rendering in High Dynamic Range is linked to the non-fixed maximum brightness value which comes with the 16-bit float values, compared to the fixed maximum of 255 in 8-bit integers. So all linear color spaces have the same advantages of HDR capabilities and advanced light calculation. The main difference between the linear color spaces are the primaries for red, green and blue. Check the Video Engine page for a detailed description.
The wider the color space, the more colors that can be represented. Where narrow color spaces, like Rec.709 are not capable of representing the same very reddish-red as an HDR color space can. The color is out-of-gamut in the SDR space. The primary values red, green and blue [(1:0:0), (0:1:0), (0:0:1)] define the look of the specific color and therefore all their mixtures. The (1:0:0) red of Rec.2020 looks much more intense compared to the (1:0:0) red of Rec.709. In fact the Rec.709 red is (0.62 : 0.06 : 0.01) in Rec.2020.
With this in mind, switching between Project Color Spaces will change the appearance of all 3D rendering colors! This is the main limitation when working with different color spaces. In general, best practice is to set it once and avoid changing it. But how do you decide?
Choosing a Color Space
For a production with known output devices, it is best to stick to the output device's color space. This ensures that Ventuz will not produce out-of-gamut colors in any of its internal rendering. However, incoming assets might be clamped if they are produced in Rec.2020. A different strategy is to choose Rec.2020 as a very wide color space, to ensure incoming assets can be processed correctly. Caution must be used when choosing colors within the 3D Rendering, to not choose colors that are outside of the output's target space. (More on this later). For mixed outputs, choosing Rec.2020 can be good strategy as well. If you are not sure and you want to render in a linear color space or stick to the more performant fixed sRGB rendering, choosing linear Rec.709 is a good option. Switching to SDR workflow, won't change the primaries and only has slightly different lighting calculation. If you decided to change later, the result would be very similar. This is also sufficient if you switch from SDR to a HDR workflow and the best option if you want to change an existing project to be HDR capable.
Output and SDR level
In general, Ventuz uses the device's output information from the EDID (for GPU outs). Because of the way the engine works, Ventuz calculates colors by referring to what's in the scene. However, the GPU's output is display referred and encodes the color values to a specific brightness in nits read from the screen. As a result, Ventuz needs a reference brightness level. The SDR-Level in the Project Properties sets the brightness of the white-point (1:1:1). If the rendering exceeds the brightness of the output device, higher values are clamped. Alternatively, you can apply tone-mapping on the Device Output to squeeze it to the range. This will usually produce better results than allowing the colors to be clamped.
Working with Color in Designer
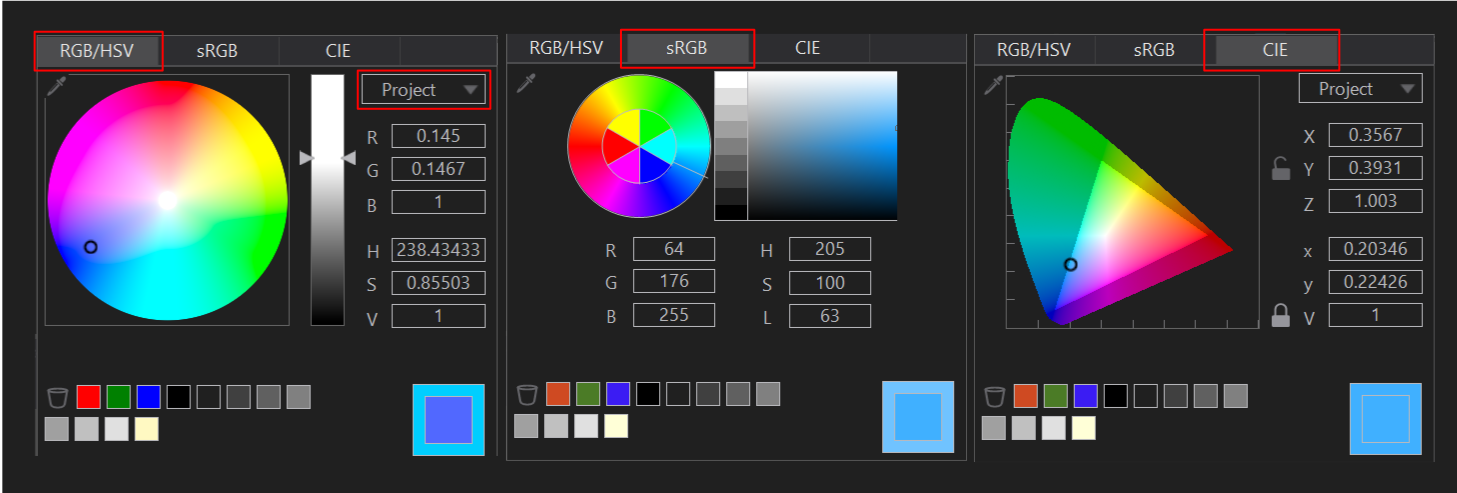
With linear color space, the Color Selector in Ventuz with different tabs and settings. The main tabs are RGB/HSV, sRGB and CIE. RGB/HSV uses a Hue and Saturation circle in combination with a Value (brightness) slider. The color shade is separated from the brightness level. The values can be set via RGB or HSV float numbers directly. This is the default tab to work in linear spaces. With the dropdown selector the color space of the Color Selector can be changed. This is a very useful feature when working in a wide space, like Rec.2020, while not exceeding the gamut of a more confined color space. E.g. if you plan to play out on a Display that supports a P3 color space, you can select this space and stay within these boundaries. The selected color value will be transformed to the Project Color Space value internally. So the RGB or HSV float values on this tab will automatically refer to the dropdown menu's selected color space. Internally all of the values will be processed in the engine's color space and also displayed in these values on a color property.
The sRGB tab functions as legacy color selector, which only uses sRGB values. Use this one to enter known sRGB int values or select a color on the picker as before. If the currently selected color value from another tab exceeds the sRGB gamut, a warning will be shown in the color picker window.
The CIE tab displays the CIE 1931 xyV/XYZ color space and value boxes. It also displays the currently selected color space gamut within CIE as highlighted rectangle. If the selected color is outside the selected color space, a warning is displayed. It is very useful, to check wether a specific color is inside a gamut and also for a better understanding of the color spaces. The xyY or XYZ values are also converted to the Project Color Space values.
Color Values: Integer vs. Float
The linear float color values are represented as (1.00 : 1.00 : 1.00) values, with a : as separator, to distinguish to the classic integer values: (255, 255, 255). Even though all color values switch to float values, the Color Converter nodes still work with integer values. Next to these, there is a float version of all these nodes to work with linear values. In general, all comma separated integer colors are in sRGB, where the float values are in the Project Color Space. All Color properties in the Property Editor have a linear category and a sRGB category with integer values. These also can be used to convert from sRGB logic to linear Project Color Space. (But only within the gamut and range of sRGB!) To enter a known sRGB int value directly you can do it via this dropdown section or simply insert the comma separated numbers or HEX values like before. To fill a color value from a string, it is still possible to bind the string with the color values to the color node. This works for linear and int values, independently of the Layer type (Standard or HDR).
Movie Clips, Live Video, Textures
On all incoming video streams, whether it is as movie clip, live video, or a single texture, Ventuz performs Input Color Processing to convert the stream to the Project's Color Space values. In general this is done automatically and Ventuz reads out the metadata of the file/stream to perform the correct transformations. With the ColorSpace property the color space, primaries and transfer function can be set manually as well as disabling the raw values. The transforms are done in real-time via a shader on the GPU. If the input color space is wider than the Project Color Space, out-of-gamut colors are clamped. Except with possible clamping, the transforms are always accurate for the whole pipe from input, via blending, to the output! With a LUT on a layer, color transformations from wider to narrow color spaces are possible.
Troubleshooting and Limitations
- The rendering on my screen looks pale, after enabling HDR:
- This might be related to the screen's limitation. Some HDR monitors can to desaturate with higher values.
- The general brightness level is too dark on my output:
- Try to increase the SDR-Level for your project to set the brightness of the standard white-point (1.00 : 1.00 : 1.00) higher and increase general luminosity
- My movie clip or texture doesn't look as I expected:
- Try checking the Color Space of the file in the Performance Statistics, to see if the video file meta-data is wrong. When in doubt, set it manually in the movie clip node.
- I can't activate HDR in Windows:
- The output screen doesn't report to Windows that it is an HDR capable display.
- Check with the manufacturer's specifications to ensure that it supports HDR.
- Check the cables and connections.
- I changed the Project Color Space and my rendering looks different now:
- With different color spaces, the primaries are different and also the color values represented. Therefore the rendered colors change. The least change between SDR and linear color space is between SDR rec.709 and linear rec.709.
- Animation channels and Remoting is fixed to integer values:
- The Scene Model is currently not expanded to work with linear color values this is also valid for the Animation node. It is possible to use Color nodes and Color Converter nodes to workaround.