Creating Realistic Reflections
Table of Contents
This page will provide you with an overview of possible ways to create reflections. We will cover the standard Mirrors and Cube Maps as well as manual camera space reflections.
Introduction
Ventuz has several nodes to create reflections, so there is no need to create a reflection setup by adding several nodes to have a reflection on your geometries. We differ between three different ways of creating a reflection: Simple Mirror, Effect Mirror, Camera Space Reflection. While the Simple- and Effect Mirror are based on the same node they still have their differences.
Simple Mirror
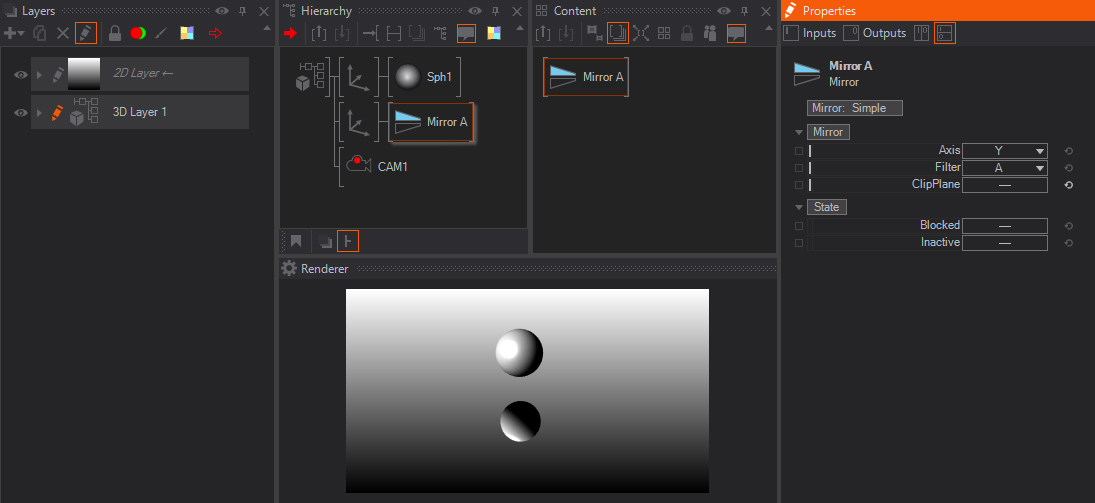
Simple Mirrors create a duplication of all 3D objects in the layer mirrored across a defined, boundless plane.
To use this type of mirror, add the Simple Mirror node to the scene and you will have a flat surface which has a simple reflection applied to it. Keep in mind that the Mirror plane is endless and can not be scaled, just rotated. The part of the surface which contains no reflection is fully transparent - therefore the created Mirror Surface can be used against a different Background or even a Layer. You can not change the color or other parameters of the reflection. The following image shows a very basic setup for a Simple Mirror.
Effect Mirror
The effect mirror is a way more advanced version of the Simple Mirror. Not only offers it a Simple Blur and Output Properties, it also has the possibility of adding any IPP Effect which we have available for Ventuz. This allows a huge freedom for your unique designs.
For the Effect Mirror its a must to have a rectangular geometry behind the mirror node. This also makes it possible to have the reflective surface oriented and transformed where you need it. Keep in mind that you can control both transforms independently, the Mirror Origin as well as the Reflective Surface.
To use the effect mirror you can simply switch the property from Mirror: Simple to Mirror: Effect or drag&drop the Mirror Effect node from the Toolbox into the Hierarchy Editor - a warning will appear and remind you to place a flat geometry behind it.
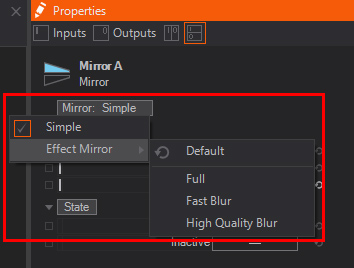
A Flat geometry can be a Rectangle or Circle.
You will notice the surface will have the reflection but its own shading color applied as well. You can adjust the appearance by adding a Material Node and adjust the properties there. After you add a material node behind, but before the flat geometry you would need to switch the lighting model from Inherit to Phong to have access to the Base and Specular properties and values.
To have a real mirror change the basecolor to Black / 0,0,0. Per default the Effect Mirror will have a Blur effect applied. You can change the Resolution to save performance (Half/Quarter) or increase the quality (Full) - the Visibility changes the overall visibility of the reflection applied to the geometry. To change the Blur you have to adjust the values in the effect section of the mirror node, here you can add more IPP-Effects as well.
The Effect Mirror will not add an endless rectangle or floor in your scene, its using a dedicated flat geometry which can be transformed freely. On top the Effect Mirror has an Output Property for the texture as well as for the size.
Use the Effect Mirror property outputs
To use the generated mirror texture output you would need to apply the texture by using e.g. a Material node, select an emissive or specular texture input and set the Mapping to Simple - ScreenAligned
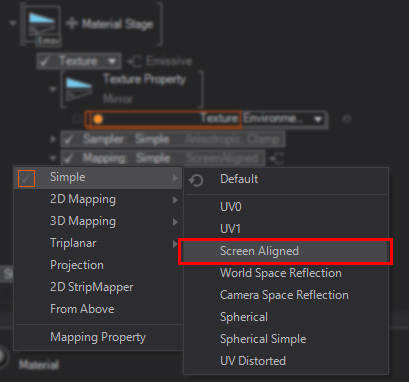
This way it is possible to have full control over the generated texture and you can make use of it as a real Material Stage. You can now assign a completely different Target for this stage, use a different blend mode or send it into a mask-channel.
Cube Maps
You can get reflections by using the RenderCubeMap node. A cube map is a six sided generated texture which can be used as a reflection source for any kind of geometry. You can generate this Cube Map each frame or just render it once. Any geometry which you append behind the RenderCubeMap node will have a cube map reflection. You adjust the intensity and appearance not only by the amount on the node itself, you can have way more control by adjusting the properties like BaseColor and Specular with a Material node. Just add the Material node between the RenderCubeMap node and the appending geometry or nodes.
Use the Cube Map texture property output
The RenderCubeMap has also an Texture Output available. Since this is a "six sided version" of a "reflection", a cross texture, you can not simply bind it to a screen aligned mapped texture slot - it uses completely different shader code. In this case you would need to add a Material node and add an IBL Specular Reflection material stage.
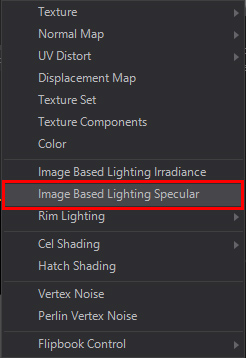
Now you can bind the Texture Property Output from the RenderCubeMap to the Texture Property from the IBL stage.
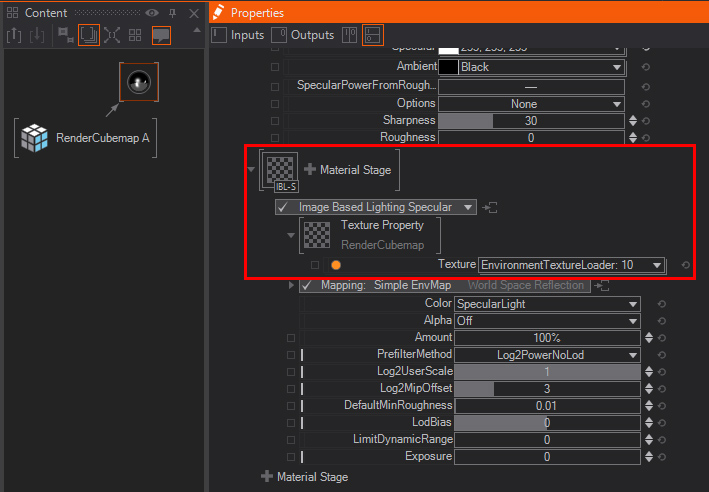
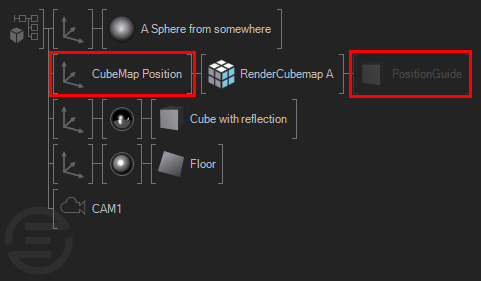
Whenever you plan to use the Cube Map Texture Property Output only, you do not need to have geometry sorted directly behind the Cube Map node. This gives you more freedom to bind the reflection where- and whenever you want. For an easier workflow you can still put a cube behind the RenderCubeMap Node to help you identify where the Cube Map reflection is rendered, i.d. the source/origin position of the reflection. Just add an Axis in front of the RenderCubeMap Node and reposition the "node" or better source position. As soon as you found the desired position you can block the geometry to hide your guide.
Conclusion
There are several ways of generating and using reflections. All have their own purpose, such as a mirror node, which will only be used for merely flat geometries such as rectangles and circles. While Cube Maps are used for generating quick and easy to use reflections on more complex geometries.
Additionally you can use the texture property outputs to modify the appearance of the generated textures. This can come in handy if you would like to alter the way you use the flat mirror.